Acute heart failure
- PMID: 32139695
- PMCID: PMC7714436
- DOI: 10.1038/s41572-020-0151-7
Acute heart failure
Abstract
Acute heart failure (AHF) is a syndrome defined as the new onset (de novo heart failure (HF)) or worsening (acutely decompensated heart failure (ADHF)) of symptoms and signs of HF, mostly related to systemic congestion. In the presence of an underlying structural or functional cardiac dysfunction (whether chronic in ADHF or undiagnosed in de novo HF), one or more precipitating factors can induce AHF, although sometimes de novo HF can result directly from the onset of a new cardiac dysfunction, most frequently an acute coronary syndrome. Despite leading to similar clinical presentations, the underlying cardiac disease and precipitating factors may vary greatly and, therefore, the pathophysiology of AHF is highly heterogeneous. Left ventricular diastolic or systolic dysfunction results in increased preload and afterload, which in turn lead to pulmonary congestion. Fluid retention and redistribution result in systemic congestion, eventually causing organ dysfunction due to hypoperfusion. Current treatment of AHF is mostly symptomatic, centred on decongestive drugs, at best tailored according to the initial haemodynamic status with little regard to the underlying pathophysiological particularities. As a consequence, AHF is still associated with high mortality and hospital readmission rates. There is an unmet need for increased individualization of in-hospital management, including treatments targeting the causative factors, and continuation of treatment after hospital discharge to improve long-term outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

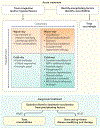
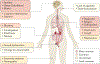
References
-
-
Ponikowski P et al. 2016 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 37, 2129–2200 (2016).
The guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology provide evidence-based recommendations on diagnosis and treatment of chronic HF and AHF.
-
-
- Braunwald E Heart failure. JACC Heart Fail. 1, 1–20 (2013). - PubMed
-
-
Mebazaa A et al. Recommendations on pre-hospital and early hospital management of acute heart failure: a consensus paper from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, the European Society of Emergency Medicine and the Society of Academic Emergency Medicine-short version. Eur. Heart J. 36, 1958–1966 (2015).
This consensus document contains contemporary recommendations endorsed by different professional societies on the management of AHF.
-
-
- Ambrosy AP et al. The global health and economic burden of hospitalizations for heart failure: lessons learned from hospitalized heart failure registries. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 63, 1123–1133 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Crespo-Leiro MG et al. European Society of Cardiology Heart Failure long-term registry (ESC-HF-LT): 1-year follow-up outcomes and differences across regions. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 18, 613–625 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

