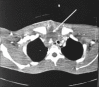
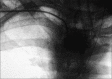
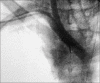
Tracheostomy creation leading to innominate artery pseudoaneurysm: A case report
- PMID: 32139940
- PMCID: PMC7017670
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.IJA_654_19
Tracheostomy creation leading to innominate artery pseudoaneurysm: A case report
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fischler L, Erhart S, Kleger GR, Frutiger A. Prevalence of tracheostomy in ICU patients. A nation-wide survey in Switzerland. Intensive Care Med. 2000;26:1428–33. - PubMed
-
- Dulguerov P, Gysin C, Perneger TV, Chevrolet JC. Percutaneous or surgical tracheostomy: A meta-analysis. Crit Care Med. 1999;27:1617–25. - PubMed
-
- Epstein SK. Late complications of tracheostomy. Respir Care. 2005;50:542–9. - PubMed
-
- Grant CA, Dempsey G, Harrison J, Jones T. Tracheo-innominate artery fistula after percutaneous tracheostomy: Three case reports and a clinical review. Br J Anaesth. 2005;96:127–31. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources