Amyloid-specific extraction using organic solvents
- PMID: 32140436
- PMCID: PMC7046812
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mex.2019.100770
Amyloid-specific extraction using organic solvents
Abstract
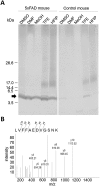
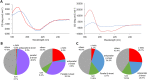
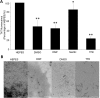
Typing of amyloidosis by mass spectrometry (MS) based proteomic analysis contribute to the diagnosis of amyloidosis. For MS analysis, laser microdissection (LMD) is used for amyloid specific sampling. This study aimed to establish a method for selectively extracting amyloids from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) specimens by organic solvent instead of LMD. The extracts using dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), dimethylformamide (DMF), methanol, trifluoroethanol (TFE) or hexafluoro-2-propanol from FFPE brain of alzheimer's disease mouse model generated protein bands on SDS-PAGE, and Aβ was identified in the extract of DMF using mass spectrometry. The extract using DMSO from the kidney of a AA amyloidosis patient produced a protein band in SDS-PAGE. This protein band was identified to be serum amyloid A (SAA) by Western blotting and mass spectrometry. Circular dichroism spectrometry revealed that the secondary structures of Aβ and transthyretin were converted to α-helices from β-sheets in TFE. Our results suggest that organic solvents can extract amyloids from FFPE specimens by converting their secondary structure. This method could eliminate the LMD step and simplified amyloid typing by MS analysis. •DMSO, DMF, methanol, TFE and HFIP can extract Aβ specifically from the FFPE brain of a Alzheimer' disease mouse model.•DMSO can extract SAA specifically from a FFPE section of AA amyloidosis.•Secondary structures of Aβ and transthyretin converted from β-sheet to α-helix in TFE.
Keywords: Amyloid; Amyloid-specific extraction from FFPE specimens using organic solvents; Formalin-fixed; Organic solvents; Paraffin-embedded; Protein extraction.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Benson M.D., Buxbaum J.N., Eisenberg D.S., Merlini G., Saraiva M.J.M., Sekijima Y., Sipe J.D., Westermark P. Amyloid nomenclature 2018: recommendations by the International Society of Amyloidosis (ISA) nomenclature committee. Amyloid. 2018;25:215–219. - PubMed
-
- Chiti F., Dobson C.M. Protein misfolding, amyloid formation, and human disease: a summary of progress over the last decade. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017;86:27–68. - PubMed
-
- Westermark P. Aspects on human amyloid forms and their fibril polypeptides. FEBS J. 2005;272:5942–5949. - PubMed
-
- Vrana J.A., Gamez J.D., Madden B.J., Theis J.D., Bergen H.R., Dogan A. Classification of amyloidosis by laser microdissection and mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis in clinical biopsy specimens. Blood. 2009;114:4957–4959. - PubMed
-
- Lavatelli F., Vrana J.A. Proteomic typing of amyloid deposits in systemic amyloidoses. Amyloid. 2011;18:177–182. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

