Finding a role for the neonatal early-onset sepsis risk calculator
- PMID: 32140673
- PMCID: PMC7046501
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2019.100255
Finding a role for the neonatal early-onset sepsis risk calculator
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Benitz and Dr. Achten declare that they have nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Kiser C., Nawab U., McKenna K., Aghai Z.H. Role of guidelines on length of therapy in chorioamnionitis and neonatal sepsis. Pediatrics. 2014;133:992–998. - PubMed
-
- Kuzniewicz M.W., Puopolo K.M., Fischer A., Walsh E.M., Li S., Newman T.B. A quantitative, risk-based approach to the management of neonatal early-onset sepsis. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171:365–371. - PubMed
-
- Schulman J., Benitz W.E., Profit J., Lee H.C., Duenas G., Bennett M.V. Newborn antibiotic exposures and association with proven infection. Pediatrics. 2019;144 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

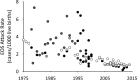
 EOS at ≤ 2 days of age,
EOS at ≤ 2 days of age,  ≤3 days of age,
≤3 days of age,  < 5 days of age,
< 5 days of age,  < 6 days of age,
< 6 days of age,  < 7 days of age.
< 7 days of age.