Association between MGMT status and response to alkylating agents in patients with neuroendocrine neoplasms: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32141507
- PMCID: PMC7098124
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20194127
Association between MGMT status and response to alkylating agents in patients with neuroendocrine neoplasms: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) is a specific DNA damage reversal repair protein. The influence of MGMT status on alkylating agent sensitivity in patients with neuroendocrine neoplasms (NENs) is controversial. We conducted a meta-analysis to assess the influence of MGMT status on the therapeutic sensitivity of alkylating agents in patients with NENs.
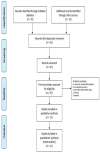
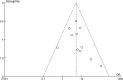
Methods: We searched PubMed, EmBase, and Cochrane library public databases through 3 July 2019. The objective response rate (ORR) was the outcome data of interest. Subgroup analysis was performed according based on MGMT methylation and expression of MGMT protein.
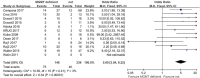
Results: Eleven studies were included in the meta-analysis. The proportion of patients with NENs that achieved an ORR after alkylating agent treatment was higher in the MGMT-deficient group than the non-deficient group (OR: 5.00; 95% CI: 3.04-8.22; P < 0.001; I2: 3%). Similar results were noted in the MGMT methylation and MGMT protein expression subgroups.
Conclusion: Patients with NENs and MGMT methylation or low protein expression had a higher ORR proportion than patients without MGMT methylation or high protein expression. The MGMT status can be used as a biological indicator of the response to alkylating agent treatment in patients with NENs.
Keywords: O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase; alkylating agents; meta-analysis; neuroendocrine neoplasms.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

