SNP rs12982687 affects binding capacity of lncRNA UCA1 with miR-873-5p: involvement in smoking-triggered colorectal cancer progression
- PMID: 32143722
- PMCID: PMC7059387
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-020-0518-0
SNP rs12982687 affects binding capacity of lncRNA UCA1 with miR-873-5p: involvement in smoking-triggered colorectal cancer progression
Abstract
Background: This investigation was arranged to elucidate whether single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of lncRNA UCA1 was implicated in elevating colorectal cancer (CRC) risk by interacting with environmental exposures.
Methods: LncRNASNP database was firstly adopted to predict SNPs that possibly affected binding of UCA1 with miRNAs and then the interactive effect of SNPs and environmental exposure on CRC risk was evaluated by recurring to type 2 gene-environment interactions (GEI) model. Besides, MTT assay, colony formation assay, transwell assay and wound healing assay were performed to assess the activity of CRC cell lines which carried distinct genotypes of specific SNPs. The impact of nicotine on activity of CRC cells was also appraised.
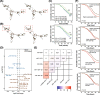
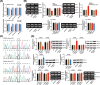
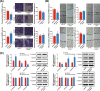
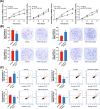
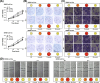
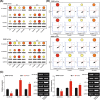
Results: SNP rs12982687 of UCA1 intervened in the binding capacity of UCA1 with several miRNAs, especially miR-873-5p. MiRNAs regulated by UCA1, as predicted by mirPath software, shared genes that were enriched in HIF1 signaling pathway. Moreover, homozygote TT of rs12982687 reduced CRC risk among smokers, and CRC cells that carried rs12982687 (CC) displayed strong migration and invasion. By contrast, miR-873-5p mimic, which reduced UCA1 expression, delayed metastasis of CRC cells (all P < 0.05). Additionally, nicotine not merely elevated UCA1 and HIF-1α expressions in CRC cells, but also facilitated proliferation and metastasis of CRC cells (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: SNP rs12982687 was involved in smoking-triggered CRC progression, given its influence on UCA1's binding with miR-873-5p and HIF-1 signaling.
Keywords: CRC; Cell migration; Cell proliferation; Gene-environment interaction; Nicotine; Single nucleotide polymorphism; lncRNA UCA1; miR-873-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
lncRNA UCA1 induced by SP1 and SP3 forms a positive feedback loop to facilitate malignant phenotypes of colorectal cancer via targeting miR-495.Life Sci. 2021 Jul 15;277:119569. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119569. Epub 2021 May 4. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33961855
-
LncRNA XIST facilitates proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells through targeting miR-486-5p and promoting neuropilin-2.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(8):13747-13761. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28054. Epub 2019 Jan 17. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30656681
-
Long noncoding RNA UCA1 regulates CCR7 expression to promote tongue squamous cell carcinoma progression by sponging miR-138-5p.Neoplasma. 2020 Nov;67(6):1256-1265. doi: 10.4149/neo_2020_191119N1187. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Neoplasma. 2020. PMID: 32749849
-
LncRNA RPLP0P2 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Proliferation and Invasion via the miR-129-5p/Zinc Finger and BTB Domain-Containing 20 Axis.Biochem Genet. 2024 Jun;62(3):1556-1576. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10478-7. Epub 2023 Aug 31. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 37651070
-
Epigenetic Regulation by lncRNAs: An Overview Focused on UCA1 in Colorectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Nov 14;10(11):440. doi: 10.3390/cancers10110440. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30441811 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SNP-Target Genes Interaction Perturbing the Cancer Risk in the Post-GWAS.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 17;14(22):5636. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225636. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of rs2107425 Polymorphism and Expression of lncH19 and miR-200a on the Susceptibility of Colorectal Cancer.Indian J Clin Biochem. 2023 Jul;38(3):331-337. doi: 10.1007/s12291-022-01052-w. Epub 2022 May 16. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2023. PMID: 37234185 Free PMC article.
-
Disparities in Recommendations for Colorectal Cancer Screening Among Average-Risk Individuals: An Ecobiosocial Approach.Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2022 May 13;15:1025-1043. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S359450. eCollection 2022. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2022. PMID: 35599752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNMT1 maintains the methylation of miR-152-3p to regulate TMSB10 expression, thereby affecting the biological characteristics of colorectal cancer cells.IUBMB Life. 2020 Nov;72(11):2432-2443. doi: 10.1002/iub.2366. Epub 2020 Sep 12. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 32918845 Free PMC article.
-
The Intergenic Type LncRNA (LINC RNA) Faces in Cancer with In Silico Scope and a Directed Lens to LINC00511: A Step toward ncRNA Precision.Noncoding RNA. 2023 Sep 25;9(5):58. doi: 10.3390/ncrna9050058. Noncoding RNA. 2023. PMID: 37888204 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

