Middle East respiratory syndrome
- PMID: 32145185
- PMCID: PMC7155742
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)33221-0
Middle East respiratory syndrome
Abstract
The Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) is a lethal zoonotic pathogen that was first identified in humans in Saudi Arabia and Jordan in 2012. Intermittent sporadic cases, community clusters, and nosocomial outbreaks of MERS-CoV continue to occur. Between April 2012 and December 2019, 2499 laboratory-confirmed cases of MERS-CoV infection, including 858 deaths (34·3% mortality) were reported from 27 countries to WHO, the majority of which were reported by Saudi Arabia (2106 cases, 780 deaths). Large outbreaks of human-to-human transmission have occurred, the largest in Riyadh and Jeddah in 2014 and in South Korea in 2015. MERS-CoV remains a high-threat pathogen identified by WHO as a priority pathogen because it causes severe disease that has a high mortality rate, epidemic potential, and no medical countermeasures. This Seminar provides an update on the current knowledge and perspectives on MERS epidemiology, virology, mode of transmission, pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical features, management, infection control, development of new therapeutics and vaccines, and highlights unanswered questions and priorities for research, improved management, and prevention.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
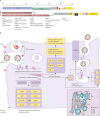
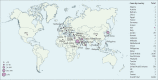
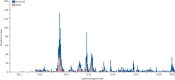

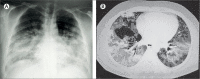
References
-
- WHO SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome) https://www.who.int/ith/diseases/sars/en/
-
- WHO Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) https://www.who.int/emergencies/mers-cov/en/
-
- WHO Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019
-
- WHO A research and development blueprint for action to prevent epidemics. https://www.who.int/blueprint/en/
-
- Peiris JS, Yuen KY, Osterhaus AD, Stöhr K. The severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2431–2441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

