Tutorial in Biostatistics: The use of generalized additive models to evaluate alcohol consumption as an exposure variable
- PMID: 32145664
- PMCID: PMC7171980
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2020.107944
Tutorial in Biostatistics: The use of generalized additive models to evaluate alcohol consumption as an exposure variable
Abstract
Alcohol consumption is a commonly studied risk factor for many poor health outcomes. Various instruments exist to measure alcohol consumption, including the AUDIT-C, Single Alcohol Screening Questionnaire (SASQ) and Timeline Followback. The information gathered by these instruments is often simplified and analyzed as a dichotomous measure, risking the loss of information of potentially prognostic value. We discuss generalized additive models (GAM) as a useful tool to understand the association between alcohol consumption and a health outcome. We demonstrate how this analytic strategy can guide the development of a regression model that retains maximal information about alcohol consumption. We illustrate these approaches using data from the Russia ARCH (Alcohol Research Collaboration on HIV/AIDS) study to analyze the association between alcohol consumption and biomarker of systemic inflammation, interleukin-6 (IL-6). We provide SAS and R code to implement these methods. GAMs have the potential to increase statistical power and allow for better elucidation of more nuanced and non-linear associations between alcohol consumption and important health outcomes.
Keywords: AUDIT-C; Alcohol consumption; Generalized additive models.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
No conflict declared.
Figures
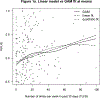

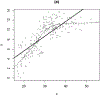


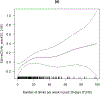

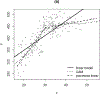

References
-
- Assessing Alcohol Problems-Second Edition [WWW Document], n.d. URL https://pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/assessingalcohol/index.htm (accessed 11.20.19).
-
- Bell S, Daskalopoulou M, Rapsomaniki E, George J, Britton A, Bobak M, Casas JP, Dale CE, Denaxas S, Shah AD, Hemingway H, 2017. Association between clinically recorded alcohol consumption and initial presentation of 12 cardiovascular diseases: population based cohort study using linked health records. BMJ 356, j909 10.1136/bmj.j909 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berhane K, Tibshirani RJ, 1998. Generalized additive models for longitudinal data. Can. J. Stat 26, 517–535. 10.2307/3315715 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

