MicroRNAs that regulate PTEN as potential biomarkers in colorectal cancer: a systematic review
- PMID: 32146564
- PMCID: PMC11804618
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-020-03172-3
MicroRNAs that regulate PTEN as potential biomarkers in colorectal cancer: a systematic review
Abstract
Purpose: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) participate in a variety of biological processes, including tumorigenesis, progression, invasion, and drug resistance to multiple cancers. Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is a cancer suppressor gene that has been certified to be regulated by miRNAs in various tumors, including colorectal cancer (CRC). In this review, we screened articles focusing on low PTEN expression in CRC, observed the expression of related miRNAs, analyzed their correlation and relationship with clinicopathological features, and discussed the possibility of these miRNAs as prognostic molecules.
Methods: We conducted a systematic search for articles published in the Web of Science, PubMed and EBSCO databases between January 1, 2002, and July 18, 2019. We identified these studies by using combinations of the following index entries and key words: 'colorectal tumor OR colorectal neoplasm OR colorectal carcinoma OR colorectal cancer OR CRC', 'protein tyrosine phosphatase OR PTEN', and 'microRNA OR MiRNA OR miRNA OR MicroRNA'. Moreover, we evaluated the underlying association between alterations in PTEN and CRC prognosis.
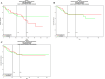
Results: PTEN expression was obviously lower in CRC tissues than in normal mucosa. However, PTEN expression did not differ significantly between adenoma and normal tissues. PTEN tends to be negatively associated with tumor size and metastasis. MiR-21, miR-200a, miR-543, miR-32, miR-92a, miR-26a, miR-106a and miR-181a were correlated with the downregulation of PTEN. MiR-26a, miR-106a and miR-181a were obviously higher in CRC tissues than in normal tissues, while PTEN was downregulated in CRC tissues. Additionally, miRNAs were mainly positively correlated with distant metastasis, followed by TNM stage. The relationship between miRNAs and tumor differentiation is controversial. However, there were no significant differences between miRNAs and either sex or age.
Conclusions: The loss of PTEN may be a diagnostic factor for CRC patients. The above-mentioned miRNAs may function as oncogenes in CRC and represent potential targets for CRC therapy. However, further prospective clinical studies are necessary.
Keywords: Biomarker; Colorectal cancer (CRC); Diagnosis; MicroRNAs (miRNAs); Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN); Prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures

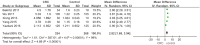
Similar articles
-
miRNA-mediated regulation of clock gene expression in men and women with colorectal cancer and possible consequences for disease management.Biomed J. 2025 Jun;48(3):100784. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2024.100784. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Biomed J. 2025. PMID: 39134242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
MicroRNA 195, lactate dehydrogenase 5, phosphatase and tensin homologue in colorectal cancer: Clinicopathology and prognosis.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2025 Jul 27;17(7):107121. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i7.107121. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2025. PMID: 40740902 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-based microRNAs as biomarkers for the diagnosis of colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Br J Cancer. 2017 Mar 14;116(6):762-774. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.12. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Br J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28152545 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the complex interplay between oral Fusobacterium nucleatum infection, periodontitis, and robust microRNA induction, including multiple known oncogenic miRNAs.mSystems. 2025 Jul 22;10(7):e0173224. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01732-24. Epub 2025 Jun 25. mSystems. 2025. PMID: 40558049 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
What Is Known about Theragnostic Strategies in Colorectal Cancer.Biomedicines. 2021 Feb 1;9(2):140. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9020140. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33535557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative Analysis of Identifying Methylation-Driven Genes Signature Predicts Prognosis in Colorectal Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Jun 11;11:629860. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.629860. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34178621 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Core Chinese Herbs against Colorectal Cancer: A Study Based on Data Mining and Network Pharmacology.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Oct 27;2020:8325076. doi: 10.1155/2020/8325076. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 33193800 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of miR-106a Regulatory Roles: from Cancer to Aging.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Jul 27;10(8):892. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10080892. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P53‑microRNA interactions regulate the response of colorectal tumor cells to oxaliplatin under normoxic and hypoxic conditions.Oncol Rep. 2023 Dec;50(6):219. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8656. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Oncol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37921068 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Society, A.C. (2018) Survival rates for colorectal cancer, by stage. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/colon-rectal-cancer/detection-diagnosis-st...
-
- Arabsorkhi Z, Gharib E, Yaghmoorian Khojini J, Farhadieh ME, Nazemalhosseini-Mojarad E, Zali MR (2019) miR-298 plays a pivotal role in colon cancer invasiveness by targeting PTEN. J Cell Physiol. 10.1002/jcp.29310 - PubMed
-
- Athanasiou T et al (2004) Off-pump myocardial revascularization is associated with less incidence of stroke in elderly patients. Ann Thorac Surg 77:745–753. 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2003.07.002 - PubMed
-
- Bakirtzi K, Hatziapostolou M, Karagiannides I, Polytarchou C, Jaeger S, Iliopoulos D, Pothoulakis C (2011) Neurotensin signaling activates microRNAs-21 and -155 and Akt, promotes tumor growth in mice, and is increased in human colon tumors. Gastroenterology 141:1749–1761. 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.038 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berania I et al (2017) Four PTEN-targeting co-expressed miRNAs and ACTN4- targeting miR-548b are independent prognostic biomarkers in human squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue. Int J Cancer 141:2318–2328. 10.1002/ijc.30915 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 81930117/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81973523/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81804073/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2017YFC1700602/a subproject of the National Key Research and Development Plan of the Ministry of Science and Technology
- 17KJA360002/the Natural Science Foundation of Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

