Complex Obstetric Perineal Injury Reconstruction Using Antropyloric Valve Transposition
- PMID: 32146790
- PMCID: PMC7069671
- DOI: 10.3393/ac.2018.08.21
Complex Obstetric Perineal Injury Reconstruction Using Antropyloric Valve Transposition
Abstract
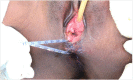
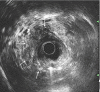
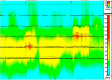
Despite significant advancements in the field of medicine, management of complex obstetric perineal injuries remains a challenge. Although several surgical techniques have been described, no techniques have provided satisfactory long-term results. Recently, a perineal transposed antropyloric valve has been used for anorectal reconstruction in patients with damaged or excised anal sphincters. We describe this technique in the case of complex obstetric perineal trauma with extensive tissue loss, presenting with end stage fecal incontinence. The functional outcome after this procedure was evaluated. The patient tolerated the surgery well, and there were no procedure-related upper gastrointestinal disturbances. Short-term functional outcomes were encouraging. At the 36-month follow-up, the patient's neoanal resting and squeeze pressures were 50 and 70 mmHg, respectively. The postoperative St. Mark's incontinence score was 7. Perineal antropyloric valve transposition is feasible and can be successfully applied in the management of end-stage fecal incontinence associated with complex obstetric perineal injury.
Keywords: Anal sphincter; Fecal incontinence; Obstetric injury; Rectovaginal fistula.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


References
-
- Altomare DF, Binda GA, Dodi G, La Torre F, Romano G, Rinaldi M, et al. Disappointing long-term results of the artificial anal sphincter for faecal incontinence. Br J Surg. 2004;91:1352–3. - PubMed
-
- Chandra A, Kumar A, Noushif M, Gupta V, Singh D, Kumar M, et al. Perineal antropylorus transposition for end-stage fecal incontinence in humans: initial outcomes. Dis Colon Rectum. 2013;56:360–6. - PubMed
-
- Keighley MR, Bick D, MacArthur C. Prevalence and obstetric factors in childbirth-related fecal incontinence (meeting abstract) Vol. 38. Dis Colon Rectum; 1995. p. 14.
-
- Tsang CB, Madoff RD, Wong WD, Rothenberger DA, Finne CO, Singer D, et al. Anal sphincter integrity and function influences outcome in rectovaginal fistula repair. Dis Colon Rectum. 1998;41:1141–6. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

