The Many Faces of Calcineurin Inhibitor Toxicity-What the FK?
- PMID: 32147003
- PMCID: PMC7080294
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ackd.2019.08.006
The Many Faces of Calcineurin Inhibitor Toxicity-What the FK?
Abstract
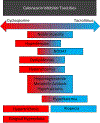
Calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs) are both the savior and Achilles' heel of kidney transplantation. Although CNIs have significantly reduced rates of acute rejection, their numerous toxicities can plague kidney transplant recipients. By 10 years, virtually all allografts will have evidence of CNI nephrotoxicity. CNIs have been strongly associated with hypertension, dyslipidemia, and new onset of diabetes after transplantation-significantly contributing to cardiovascular risk in the kidney transplant recipient. Multiple electrolyte derangements including hyperkalemia, hypomagnesemia, hypercalciuria, metabolic acidosis, and hyperuricemia may be challenging to manage for the clinician. Finally, CNI-associated tremor, gingival hyperplasia, and defects in hair growth can have a significant impact on the transplant recipient's quality of life. In this review, the authors briefly discuss the pharmacokinetics of CNI and discuss the numerous clinically relevant toxicities of commonly used CNIs, cyclosporine and tacrolimus.
Keywords: Calcineurin inhibitors; Cyclosporine; Drug toxicity; Kidney transplantation; Tacrolimus.
Copyright © 2019 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose
Figures
References
-
- Hart A, Smith JM, Skeans MA, et al. OPTN/SRTR 2017 Annual Data Report: Kidney. Am J Transplant. 2019;19 Suppl 2: 19–123. - PubMed
-
- Rovin BH, Solomons N, Pendergraft WF 3rd, et al. A randomized, controlled double-blind study comparing the efficacy and safety of dose-ranging voclosporin with placebo in achieving remission in patients with active lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2019;95(1): 219–231. - PubMed
-
- Cattran DC, Appel GB, Hebert LA, et al. Cyclosporine in patients with steroid-resistant membranous nephropathy: a randomized trial. Kidney Int. 2001;59(4): 1484–1490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical