Analysis of the Effect of Nine Consecutive Years' Intensive Management and Number of Times Achieving the Target Control on Endpoint Events in T2DM Patients in Sanlitun Community Health Service Center in Beijing
- PMID: 32148488
- PMCID: PMC7053495
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/3646342
Analysis of the Effect of Nine Consecutive Years' Intensive Management and Number of Times Achieving the Target Control on Endpoint Events in T2DM Patients in Sanlitun Community Health Service Center in Beijing
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of intensive management and achieving the target control more than 3 times on endpoint events during 9 consecutive years' annual assessment in type 2 diabetes (T2DM) patients in the Sanlitun Community Health Service Center in Beijing, including blood glucose, blood pressure, lipids profiles, and the joint target control.
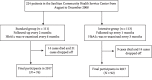
Methods: In Beijing Community Diabetes Study (BCDS), 224 patients with T2DM from the Sanlitun Community Health Service Center were enrolled in 2008. All patients were randomly assigned to the intensive management group (n = 113) and the standard management group (n = 113) and the standard management group (.
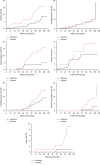
Results: During the nine-year follow-up, the abscission number was 35 (14.29%), among which 14 (12.39%) was in the intensive management group and 21 (18.92%) was in the standard management group. The incidence of diabetic retinopathy (6 cases, 5.41%) and diabetic nephropathy (13 cases, 11.71%) in the standard management group was significantly higher than that in the intensive management group (1 case, 0.88%; 5 cases, 4.42%), respectively (P < 0.05). However, there were no significant differences on the other endpoint events between the two groups (P < 0.05). However, there were no significant differences on the other endpoint events between the two groups (P < 0.05). However, there were no significant differences on the other endpoint events between the two groups (P < 0.05). However, there were no significant differences on the other endpoint events between the two groups (P < 0.05). However, there were no significant differences on the other endpoint events between the two groups (.
Conclusions: The intensive management can effectively reduce the occurrence of microvascular complications. The incidence of all-cause death and the other endpoint events decreased in T2DM patients who achieved the joint target control more than 3 times during the nine-year management, which improved survival time and life quality. This trial is registered with ChiCTR-TRC-13003978 and ChiCTR-OOC-15006090.
Copyright © 2020 Chen-Mei Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Listed N. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2017: summary of revisions. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(1):s4–s5. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2017. Diabetes Care. 2017;40(1):S1–S135.
-
- Zhuang N., Zhang J. D., Wan G., et al. An eight-year cohort study of the effect of the joint control on cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Chinese General Practice. 2017;20(25):3109–3l16.
-
- Chinese Diabetes Society. Chinese guideline for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (2010 edition) Chinese Joumal of the Fmntiers of Medical Science (Electmnic Version) 2011;3(6):54–109.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources