Clarithromycin-Associated Acute Liver Failure Leading to Fatal, Massive Upper Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage from Profound Coagulopathy: Case Report and Systematic Literature Review
- PMID: 32148980
- PMCID: PMC7049424
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/2135239
Clarithromycin-Associated Acute Liver Failure Leading to Fatal, Massive Upper Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage from Profound Coagulopathy: Case Report and Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
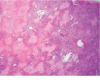
While erythromycin has caused numerous cases of acute liver failure (ALF), clarithromycin, a similar macrolide antibiotic, has caused only six reported cases of ALF. A new case of clarithromycin-associated ALF is reported with hepatic histopathology and exclusion of other etiologies by extensive workup, and the syndrome of clarithromycin-associated ALF is better characterized by systematic review. A 60-year-old nonalcoholic man, with normal baseline liver function tests, was admitted with diffuse abdominal pain and AST = 499 U/L and ALT = 539 U/L, six days after completing a 7-day course of clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily for suspected upper respiratory infection. AST and ALT each rose to about 1,000 U/L on day-2 of admission, and rose to ≥6,000 U/L on day-3, with development of severe hepatic encephalopathy and severe coagulopathy. Planned liver biopsy was cancelled due to coagulopathies. Extensive evaluation for infectious, immunologic, and metabolic causes of liver disease was negative. Abdominal computerized tomography and abdominal ultrasound with Doppler were unremarkable. The patient developed massive, acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding associated with coagulopathies. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy was planned after massive blood product transfusions, but the patient rapidly expired from hemorrhagic shock. Autopsy revealed a golden-brown heavy liver with massive hepatic necrosis and sinusoidal congestion. Rise of AST/ALT to about 1,000 U/L each was temporally incompatible with shock liver because this rise preceded the hemorrhagic shock, but the subsequent AST/ALT rise to ≥6,000 U/L each may have had a component of shock liver. The six previously reported cases were limited by failure to exclude hepatitis E (4), lack of liver biopsy (2), and uninterpretable liver biopsy (1) and by confounding potential etiologies including disulfiram, israpidine, or recent acetaminophen use (3), clarithromycin overdose (1), active alcohol use (1), and severe heart failure (1). Review of 6 previously reported and current case of clarithromycin-associated ALF revealed that patients had AST and ALT values in the thousands. Five patients died and 2 survived.
Copyright © 2020 Ahmed I. Edhi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Shaheen N., Grimm I. S. Fulminant hepatic failure associated with clarithromycin. The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 1996;91(2):394–395. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

