Multivalent Polymer-Peptide Conjugates-A General Platform for Inhibiting Amyloid Beta Peptide Aggregation
- PMID: 32149017
- PMCID: PMC7059649
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmacrolett.9b00559
Multivalent Polymer-Peptide Conjugates-A General Platform for Inhibiting Amyloid Beta Peptide Aggregation
Abstract
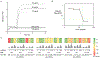
Protein aggregation is implicated in multiple deposition diseases including Alzheimer's Disease, which features the formation of toxic aggregates of amyloid beta (Aβ) peptides. Many inhibitors have been developed to impede or reverse Aβ aggregation. Multivalent inhibitors, however, have been largely overlooked despite the promise of high inhibition efficiency endowed by the multivalent nature of Aβ aggregates. In this work, we report the success of multivalent polymer-peptide conjugates (mPPCs) as a general class of inhibitors of the aggregation of Aβ40. Significantly delayed onset of fibril formation was realized using mPPCs prepared from three peptide/peptoid ligands covering a range of polymer molecular weights (MWs) and ligand loadings. Dose dependence studies showed that the nature of the ligands is a key factor in mPPC inhibition potency. The negatively charged ligand LPFFD (LD) leads to more efficient mPPCs compared to the neutral ligands, and is most effective at 7% ligand loading across different MWs. Molecular dynamics simulations along with dynamic light scattering experiments suggest that mPPCs form globular structures in solution due to ligand-ligand interactions. Such interactions are key to the spatial proximity of ligands and thus to the multivalency effect of mPPC inhibition. Excess ligand-ligand interactions, however, reduce the accessibility of mPPC ligands to Aβ peptides, and impair the overall inhibition potency.
Figures
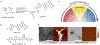


References
-
- Glenner GG; Wong CW Alzheimer’s Disease: Initial Report of the Purification and Characterization of a Novel Cerebrovascular Amyloid Protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 1984, 120, 885–890. - PubMed
-
- Han X; He G Toward a Rational Design to Regulate β-Amyloid Fibrillation for Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment. ACS Chem. Neurosci 2018, 9, 198–210. - PubMed
-
- Goyal D; Shuaib S; Mann S; Goyal B Rationally Designed Peptides and Peptidomimetics as Inhibitors of Amyloid-β (Aβ) Aggregation: Potential Therapeutics of Alzheimer’s Disease. ACS Comb Sci 2017, 19, 55–80. - PubMed
-
- Sun H; Liu J; Li S; Zhou L; Wang J; Liu L; Lv F; Gu Q; Hu B; Ma Y; Wang S Reactive Amphiphilic Conjugated Polymers for Inhibiting Amyloid β Assembly. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2019, 58, 5988–5993. - PubMed
-
- Cabaleiro-Lago C; Quinlan-Pluck F; Lynch I; Lindman S; Minogue AM; Thulin E; Walsh DM; Dawson KA; Linse S Inhibition of Amyloid β Protein Fibrillation by Polymeric Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2008, 130, 15437–15443. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

