Early Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of 28 Cases of Coronavirus Disease in South Korea
- PMID: 32149037
- PMCID: PMC7045878
- DOI: 10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.1.03
Early Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of 28 Cases of Coronavirus Disease in South Korea
Abstract
Objectives: The first confirmed case of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in South Korea was reported in January 2020, with 28 confirmed cases reported as of February 14th, 2020. The epidemiological and clinical characteristics of all 28 cases were analyzed in response to this disease.
Methods: The epidemiological characteristics and early clinical features of the 28 patients from Korea with confirmed COVID-19 were analyzed using COVID-19 reporting and surveillance data and the epidemiological investigation reports prepared by the rapid response team.
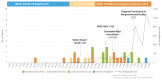
Results: There were 16 patients that entered Korea from foreign countries: Wuhan, China (11 patients), Zhuhai, China, (1 patient), Singapore (2 patients), Japan (1 patient), and Thailand (1 patient). The early symptoms were fever, sore throat, cough or sputum production, chills, and muscle ache. Three patients were asymptomatic, however, 18 developed pneumonia. Of the 28 cases, 16 were index cases imported from abroad, with 10 cases of secondary infection originating in Korea, and the route of transmission still under investigation for 2 patients. The 10 patients with secondary infection were infected from contact with family members or acquaintances of primary patients, and the suspected sites of transmission were mostly at home.
Conclusion: COVID-19 in Korea was spread by 16 infected individuals traveling from other countries, leading to second-generation cases. The initial symptoms were mostly minor, but the disease was infectious at this stage, resulting from close contact, particularly at home. Establishing an early detection strategy for COVID-19 is crucial for managing the transmission of the disease.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; epidemiologic study.
Copyright ©2020, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization [Internet] Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Situation reports. Geneva (Switzerland): World Health Organization; 2020. [cited 2020 Feb 17]. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio....
-
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [Internet] COVID-19: Health alerts, the fastest updates. Cheongju (Korea): Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2020. [cited 2020 Feb 14]. Available from: http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/tcmBoardList.do?brdId=&brdGubun=&dataGubun=&ncvCo...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous