Norvaline Reduces Blood Pressure and Induces Diuresis in Rats with Inherited Stress-Induced Arterial Hypertension
- PMID: 32149110
- PMCID: PMC7042509
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/4935386
Norvaline Reduces Blood Pressure and Induces Diuresis in Rats with Inherited Stress-Induced Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
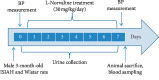
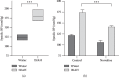
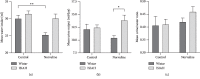
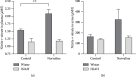
Growing evidence suggests that increased arginase activity affects vital bioprocesses in various systems and universally mediates the pathogenesis of numerous metabolic diseases. The adverse effects of arginase are associated with a severe decline in L-arginine bioavailability, which leads to nitric oxide synthase substrate insufficiency, uncoupling, and, eventually, superoxide anion generation and substantial reduction of nitric oxide (NO) synthesis. In cooperation, it contributes to chronic oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction, which might lead to hypertension and atherosclerosis. Recent preclinical investigations point arginase as a promising therapeutic target in ameliorating metabolic and vascular dysfunctions. In the present study, adult rats with inherited stress-induced arterial hypertension (ISIAH) were used as a model of hypertension. Wistar rats served as normotensive controls. Experimental animals were intraperitoneally administered for seven days with nonproteinogenic amino acid L-norvaline (30 mg/kg/day), which is a potent arginase inhibitor, or with the vehicle. Blood pressure (BP), body weight, and diuresis were monitored. The changes in blood and urine levels of creatinine, urea, and NO metabolites were analyzed. We observed a significant decline in BP and induced diuresis in ISIAH rats following the treatment. The same procedure did not affect the BP of control animals. Remarkably, the treatment had no influence upon glomerular filtration rate in two experimental groups, just like the daily excretion of creatinine and urea. Conversely, NO metabolite levels were amplified in normotonic but not in hypertensive rats following the treatment. The data indicate that L-norvaline is a potential antihypertensive agent and deserves to be clinically investigated. Moreover, we suggest that changes in blood and urine are causally related to the effect of L-norvaline upon BP regulation.
Copyright © 2020 Michael A. Gilinsky et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

