Structural basis for pharmacological modulation of the TRPC6 channel
- PMID: 32149605
- PMCID: PMC7082128
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.53311
Structural basis for pharmacological modulation of the TRPC6 channel
Abstract
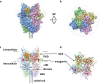
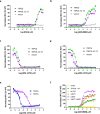
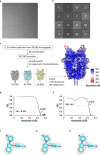
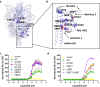
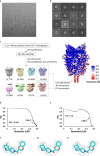
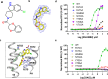
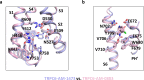
Transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) proteins form nonselective cation channels that play physiological roles in a wide variety of cells. Despite growing evidence supporting the therapeutic potential of TRPC6 inhibition in treating pathological cardiac and renal conditions, mechanistic understanding of TRPC6 function and modulation remains obscure. Here we report cryo-EM structures of TRPC6 in both antagonist-bound and agonist-bound states. The structures reveal two novel recognition sites for the small-molecule modulators corroborated by mutagenesis data. The antagonist binds to a cytoplasm-facing pocket formed by S1-S4 and the TRP helix, whereas the agonist wedges at the subunit interface between S6 and the pore helix. Conformational changes upon ligand binding illuminate a mechanistic rationale for understanding TRPC6 modulation. Furthermore, structural and mutagenesis analyses suggest several disease-related mutations enhance channel activity by disrupting interfacial interactions. Our results provide principles of drug action that may facilitate future design of small molecules to ameliorate TRPC6-mediated diseases.
Keywords: Cryo-EM; drug discovery; human; molecular biophysics; structural biology.
© 2020, Bai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
YB At the time of the study YB was affiliated with Amgen Research, Amgen Inc and has no financial interests to declare. The author has no other competing interests to declare. XY XY is affiliated with Amgen Research, Amgen Inc and has no financial interests to declare. The author has no other competing interests to declare. HC At the time of the study HC was affiliated with Amgen Research, Amgen Inc and has no financial interests to declare. The author has no other competing interests to declare. DH At the time of the study DH was affiliated with Amgen Research, Amgen Inc and has no financial interests to declare. The author has no other competing interests to declare. RW At the time of the study RW was affiliated with Amgen Research, Amgen Inc and has no financial interests to declare. The author has no other competing interests to declare. XW XW is affiliated with Amgen Research, Amgen Inc and has no financial interests to declare. The author has no other competing interests to declare. PL At the time of the study PL was affiliated with Amgen Research, Amgen Inc and has no financial interests to declare. The author has no other competing interests to declare. YG At the time of the study YG was affiliated with Amgen Research, Amgen Inc and has no financial interests to declare. The author has no other competing interests to declare. SG SGR is affiliated with Amgen Research, Amgen Inc and has no financial interests to declare. The author has no other competing interests to declare. DL DCL is affiliated with Amgen Research, Amgen Inc and has no financial interests to declare. The author has no other competing interests to declare. XH At the time of the study XH was affiliated with Amgen Research, Amgen Inc and has no financial interests to declare. The author has no other competing interests to declare.
Figures







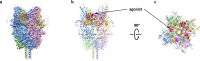







References
-
- Afonine PV, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Moriarty NW, Mustyakimov M, Terwilliger TC, Urzhumtsev A, Zwart PH, Adams PD. Towards automated crystallographic structure refinement with phenix.refine. Acta Crystallographica Section D Biological Crystallography. 2012;68:352–367. doi: 10.1107/S0907444912001308. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen VB, Arendall WB, Headd JJ, Keedy DA, Immormino RM, Kapral GJ, Murray LW, Richardson JS, Richardson DC. MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallographica Section D Biological Crystallography. 2010;66:12–21. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909042073. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

