Claudin-2 deficiency associates with hypercalciuria in mice and human kidney stone disease
- PMID: 32149733
- PMCID: PMC7108907
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI127750
Claudin-2 deficiency associates with hypercalciuria in mice and human kidney stone disease
Abstract
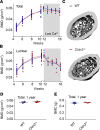
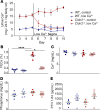
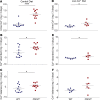
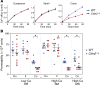
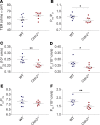
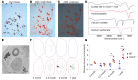
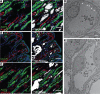
The major risk factor for kidney stone disease is idiopathic hypercalciuria. Recent evidence implicates a role for defective calcium reabsorption in the renal proximal tubule. We hypothesized that claudin-2, a paracellular cation channel protein, mediates proximal tubule calcium reabsorption. We found that claudin-2-null mice have hypercalciuria due to a primary defect in renal tubule calcium transport and papillary nephrocalcinosis that resembles the intratubular plugs in kidney stone formers. Our findings suggest that a proximal tubule defect in calcium reabsorption predisposes to papillary calcification, providing support for the vas washdown hypothesis. Claudin-2-null mice were also found to have increased net intestinal calcium absorption, but reduced paracellular calcium permeability in the colon, suggesting that this was due to reduced intestinal calcium secretion. Common genetic variants in the claudin-2 gene were associated with decreased tissue expression of claudin-2 and increased risk of kidney stones in 2 large population-based studies. Finally, we describe a family in which males with a rare missense variant in claudin-2 have marked hypercalciuria and kidney stone disease. Our findings indicate that claudin-2 is a key regulator of calcium excretion and a potential target for therapies to prevent kidney stones.
Keywords: Calcium; Cell Biology; Epithelial transport of ions and water; Nephrology; Transport.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Claudin 2: role in hypercalciuria and kidney stone disease.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020 May;16(5):252. doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-0273-x. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32210380 No abstract available.
-
Claudin 2 and hypercalciuria - of mice and men.Nat Rev Urol. 2020 May;17(5):255. doi: 10.1038/s41585-020-0318-8. Nat Rev Urol. 2020. PMID: 32273584 No abstract available.
-
Re: Claudin-2 Deficiency Associates with Hypercalciuria in Mice and Human Kidney Stone Disease.J Urol. 2020 Aug;204(2):379-380. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000001112. Epub 2020 May 12. J Urol. 2020. PMID: 32396431 No abstract available.
-
Genetic variation in claudin-2, hypercalciuria, and kidney stones.Kidney Int. 2020 Nov;98(5):1076-1078. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.05.055. Epub 2020 Jul 10. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 32653401 No abstract available.
-
Re: Claudin-2 Deficiency Associates with Hypercalciuria in Mice and Human Kidney Stone Disease.J Urol. 2020 Oct;204(4):882-883. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000001222.02. Epub 2020 Jul 27. J Urol. 2020. PMID: 32716223 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

