Otosyphilis: A Review of the Literature
- PMID: 32149965
- PMCID: PMC8530448
- DOI: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001155
Otosyphilis: A Review of the Literature
Abstract
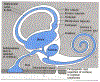
The number of cases of syphilis has increased in the United States and in many high-income nations. Otosyphilis is a less recognized complication of syphilis that can lead to irreversible sensorineural hearing loss. Different pathophysiological mechanisms have been proposed to explain hearing loss in otosyphilis. We review the literature on otosyphilis in adults and propose the need for future work in this field to identify better ways to diagnose, treat, and manage this disease. Patients with syphilis should be screened routinely for hearing loss, and all patients with new, sudden, or fluctuating sensorineural hearing loss should be evaluated for syphilis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control Prevention. Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/std/treatment/default.htm.
-
- Wasserheit J Epidemiologic synergy: interrelationships between human immunodeficiency virus infection and other sexually transmitted diseases. Sex Transm Dis 1992;19:61–77. - PubMed
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Syphilis and congenital syphilis in Europe. A review of epidemiological trends (2007–2018) and options for response. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/Syphilis-and-co....
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance 2018. Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; 2019. DOI: 10.15620/cdc.79370. - DOI
-
- Theeuwen H, Whipple M, Litvack JR. Otosyphilis: Resurgence of an Old Disease. The Laryngoscope 2018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical