Transmission center and driving factors of hand, foot, and mouth disease in China: A combined analysis
- PMID: 32150558
- PMCID: PMC7062235
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008070
Transmission center and driving factors of hand, foot, and mouth disease in China: A combined analysis
Abstract
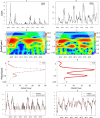
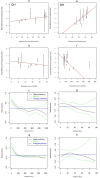
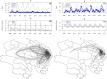
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) has become a major public health issue in China. The disease incidence varies substantially over time and across space. To understand the heterogeneity of HFMD transmission, we compare the spatiotemporal dynamics of HFMD in Qinghai and Shanghai by conducting combined analysis of epidemiological, wavelet time series, and mathematical methods to county-level data from 2009 to 2016. We observe hierarchical epidemic waves in Qinghai, emanating from Huangzhong and in Shanghai from Fengxian. Besides population, we also find that the traveling waves are significantly associated with socio-economic and geographical factors. The population mobility also varies between the two regions: long-distance movement in Qinghai and between-neighbor commuting in Shanghai. Our findings provide important evidence for characterizing the heterogeneity of HFMD transmission and for the design and implementation of interventions, such as deploying optimal vaccine and changing local driving factors in the transmission center, to prevent or limit disease spread in these areas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures