Neuroprotective effect of menaquinone-4 (MK-4) on transient global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat
- PMID: 32150581
- PMCID: PMC7062268
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229769
Neuroprotective effect of menaquinone-4 (MK-4) on transient global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat
Abstract
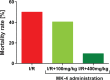
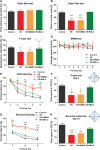
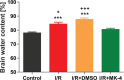
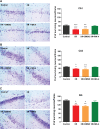
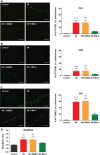
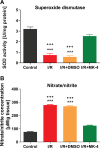
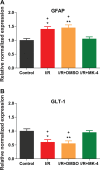
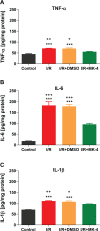
Cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury causes cognitive deficits, excitotoxicity, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and brain edema. Vitamin K2 (Menaquinone 4, MK-4) as a potent antioxidant can be a good candidate to ameliorate I/R consequences. This study focused on the neuroprotective effects of MK-4 for cerebral I/R insult in rat's hippocampus. The rat model of cerebral I/R was generated by transient bilateral common carotid artery occlusion for 20 min. Rats were divided into control, I/R, I/R+DMSO (solvent (1% v/v)) and I/R+MK-4 treated (400 mg/kg, i.p.) groups. Twenty-four hours after I/R injury induction, total brain water content, superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, nitrate/nitrite concentration and neuronal density were evaluated. In addition to quantify the apoptosis processes, TUNEL staining, as well as expression level of Bax and Bcl2, were assessed. To evaluate astrogliosis and induced neurotoxicity by I/R GFAP and GLT-1 mRNA expression level were quantified. Furthermore, pro-inflammatory cytokines including IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α were measured. Seven days post I/R, behavioral analysis to quantify cognitive function, as well as Nissl staining for surviving neuronal evaluation, were conducted. The findings indicated that administration of MK-4 following I/R injury improved anxiety-like behavior, short term and spatial learning and memory impairment induced by I/R. Also, MK-4 was able to diminish the increased total brain water content, apoptotic cell density, Bax/ Bcl2 ratio and GFAP mRNA expression following I/R. In addition, the high level of nitrate/nitrite, IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α induced by I/R was reduced after MK-4 administration. However, MK-4 promotes the level of SOD activity and GLT-1 mRNA expression in I/R rat model. The findings demonstrated that MK-4 can rescue transient global cerebral I/R consequences via its anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative stress features. MK-4 administration ameliorates neuroinflammation, neurotoxicity and neuronal cell death processes and leads to neuroprotection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Ma J, Liu Z, Shi Z. Oxidative Stress and Nitric Oxide in Cerebral Ischemic Reperfusion Injury Cerebral Ischemic Reperfusion Injuries (CIRI): Springer; 2018. p. 101–19.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

