Prognostic significance of the radiologic features of pneumonitis induced by anti-PD-1 therapy
- PMID: 32150668
- PMCID: PMC7196069
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.2974
Prognostic significance of the radiologic features of pneumonitis induced by anti-PD-1 therapy
Abstract
Background: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) induced by anti-programmed-cell death-1 (PD-1) and anti-PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is potentially life-threatening and is a common reason of the discontinuation of therapy. In contrast, an enhancement in antitumor effects was reported in patients who developed immune-related adverse events, including ILD. Although recent evidence suggests that radiologic patterns of ILD may reflect the severity of ILD and the antitumor immune responses to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapies, the association between radiologic features and clinical outcomes remains unclear.
Methods: Patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer who were treated with 1st to 3rd line anti-PD-1 therapy from January 2016 through October 2017 were identified at multiple institutions belonging to the Niigata Lung Cancer Treatment Group. ILD was diagnosed by the treating physicians, and chest computed tomography scans were independently reviewed to assess the radiologic features of ILD.
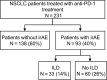
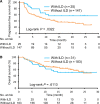
Results: A total of 231 patients who received anti-PD-1 therapy were enrolled. Thirty-one patients (14%) developed ILD. Sixteen patients were classified as having ground glass opacities (GGO), 16 were classified as having cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP), and one was classified as having pneumonitis not otherwise specified. Patients with GGO had significantly worse overall survival time compared to patients with COP (7.8 months (95% CI: 2.2-NE) versus not reached (95% CI: 13.2-NE); P = 0.0175). Multivariate analysis of all 231 patients also revealed that PS = 1 and ≥2 and GGO were significant predictors of a worse overall survival.
Conclusions: This study demonstrated that patients who developed GGO exhibited worse outcomes among non-small-cell lung cancer patients receiving anti-PD-1 therapies.
Keywords: NSCLC; PD-1; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immune-related adverse event; interstitial lung disease.
© 2020 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Watanabe received lecture fees from Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Novartis Pharma, AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharma, Bristol‐Myers, Boehringer Ingelheim, MSD, Ono Pharmaceutical, Daiichi Sankyo and Taiho Pharmaceutical; Dr Ota received lecture fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, MSD, Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca and Chugai Pharma; Dr Hayashi received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Ono Pharmaceutical, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo, Taiho Pharmaceutical and Actelion Pharmaceuticals Japan; Dr Ishikawa received lecture fees from Daiichi Sankyo, Bayer, Nihon Medi‐Physics and AstraZeneca; Dr Shoji received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharma, Taiho Pharmaceutical and MSD; Dr Nozaki received lecture fees from Bristol‐Myers, Pfizer and Novartis; Dr Ichikawa received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharma, Bristol‐Myers, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ono Pharmaceutical and Taiho Pharmaceutical; Dr Miyabayashi received lecture fees from Chugai Pharma, Ono Pharmaceutical, AstraZeneca and Actelion Pharmaceuticals; Dr Miura received lecture fees from Bristol‐Myers, Ono Pharmaceutical, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, MSD, Chugai Pharma, AstraZeneca, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Hakko Kirin and Mochida Pharmaceutical; Dr Tanaka received lecture fees and grants from Bristol‐Myers, Eli Lilly, MSD, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Pfizer, Chugai Pharma, Ono Pharmaceutical, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, lecture fees from Novartis and grant from Merck Serono; Dr Abe received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Taiho Pharmaceutical and Bristol‐Myers; Dr Okajima received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Ono Pharmaceutical, Bristol‐Myers, Boehringer Ingelheim, MSD and Taiho Pharmaceutical; Dr Terada received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharma, Bristol‐Myers, Boehringer Ingelheim, Taiho Pharmaceutical, MSD and Ono Pharmaceutical; Dr Ishida received lecture fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol‐Myers, Chugai Pharma, Eli Lilly and AstraZeneca; Dr Iwashima received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Chugai Pharma, Bristol‐Myers, Boehringer Ingelheim, Taiho Pharmaceutical, MSD, Ono Pharmaceutical, Novartis, Actelion Pharmaceuticals, Torii Pharmaceutical and KYORIN Pharmaceutical; Dr Sato received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ono Pharmaceutical, MSD and Pfizer; Dr Yoshizawa received lecture fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Chugai Pharma and Ono Pharmaceutical; Dr Kikuchi received grant and lecture fees from Chugai Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, MSD, Taiho Pharmaceutical, Daiichi Sankyo, Ono Pharmaceutical AstraZeneca, Shionogi, TEIJIN PHARMA and KYORIN Pharmaceutical, and lecture fees from Astellas Pharma, Bristol‐Myers, Pfizer, Taisho Toyama Pharmaceutical, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Japan BCG Laboratory Novartis, Mylan NV and Roche Diagnostics. All remaining authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Herbst RS, Baas P, Kim D‐W, et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD‐L1‐positive, advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE‐010): a randomised controlled trial. The Lancet. 2016;387:1540‐1550. - PubMed
-
- Reck M, Rodríguez‐Abreu D, Robinson AG, et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD‐L1‐positive non‐small‐cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1823‐1833. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

