Elsholtzia ciliata (Thunb.) Hyl. Extracts from Different Plant Parts: Phenolic Composition, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities
- PMID: 32150805
- PMCID: PMC7179165
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25051153
Elsholtzia ciliata (Thunb.) Hyl. Extracts from Different Plant Parts: Phenolic Composition, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities
Abstract
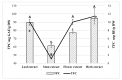
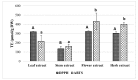
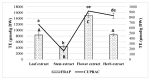
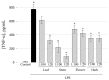
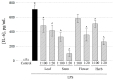
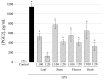
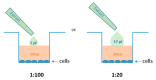
Polyphenols play an important role on the health-promoting properties of humans. Plants belonging to Lamiaceae family are known as rich source of phenolic compounds. The current work aimed to evaluate the phenolic compounds, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activity of Elsholtzia ciliata (Thunb.) Hyl. ethanolic extracts from leaf, stem, flower, and whole herb. Twelve compounds were identified in ethanolic extracts using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The HPLC analysis revealed that chlorogenic acid, rosmarinic acid, and rutin were predominant compounds in ethanolicic extracts. Using HPLC-ABTS (2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)) post-column assay, avicularin, chlorogenic, and rosmarinic acids were identified as the predominant radical scavengers in all ethanolic extracts. All tested preparations significantly reduced the level of secretion of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and prostaglandin E2 induced by lipopolysaccharide treatment in mouse peritoneal macrophage cell culture. Stem and flower extracts were most efficient in reducing cytokine release, but leaf extract demonstrated stronger effect on prostaglandin E2 secretion. This is the first study exploring antioxidant efficiency by HPLC-ABTS post-column method and investigating anti-inflammatory activity of ethanolic extracts from E. ciliata different plant parts.
Keywords: Elsholtzia ciliata; HPLC–ABTS post-column; anti-inflammatory activity; antioxidant; natural compounds; polyphenols; rosmarinic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Skendi A., Irakli M., Chatzopoulou P. Analysis of phenolic compounds in Greek plants of Lamiaceae family by HPLC. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants. 2017;6:62–69. doi: 10.1016/j.jarmap.2017.02.001. - DOI
-
- Fiorentino A., DellaGreca M., D’Abrosca B., Oriano P., Golino A., Izzo A., Zarrelli A., Monaco P. Lignans, neolignans and sesquilignans from Cestrum parqui l’Her. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2007;35:392–396. doi: 10.1016/j.bse.2006.12.009. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

