Oxylipin Profiles as Functional Characteristics of Acute Inflammatory Responses in Astrocytes Pre-Treated with IL-4, IL-10, or LPS
- PMID: 32150861
- PMCID: PMC7084882
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21051780
Oxylipin Profiles as Functional Characteristics of Acute Inflammatory Responses in Astrocytes Pre-Treated with IL-4, IL-10, or LPS
Abstract
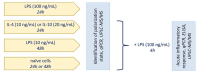
Functional phenotypes, which cells can acquire depending on the microenvironment, are currently the focus of investigations into new anti-inflammatory therapeutic approaches. Glial cells, microglia, and astrocytes are major participants in neuroinflammation, but their roles differ, as microglia are cells of mesodermal origin, while astrocytes are cells of ectodermal origin. The inflammatory phenotype of cells can be modulated by ω-6- and ω-3-polyunsaturated fatty acid-derived oxylipins, although data on changes in oxylipin profiles in different cell adaptations to pro- and anti-inflammatory stimuli are scarce. Our study aimed to compare UPLC-MS/MS-measured oxylipin profiles in various rat astrocyte adaptation states. We used cells treated for 24 h with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for classical pro-inflammatory adaptation and with interleukin 4 (IL-4) or 10 (IL-10) for alternative anti-inflammatory adaptation, with the resulting phenotypes characterized by quantitative real-time PCR (RT-PCR). We also tested long-term, low-concentration LPS treatment (endotoxin treatment) as a model of astrocyte adaptations. The functional response of astrocytes was estimated by acute (4 h) LPS-induced cell reactivity, measured by gene expression markers and oxylipin synthesis. We discovered that, as well as gene markers, oxylipin profiles can serve as markers of pro- (A1-like) or anti-inflammatory (A2-like) adaptations. We observed predominant involvement of ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) and the cyclooxygenase branch for classical (LPS) pro-inflammatory adaptations and ω-3 PUFA and the lipoxygenase branch for alternative (IL-4) anti-inflammatory adaptations. Treatment with IL-4, but not IL-10, primes the ability of astrocytes to activate the innate immunity signaling pathways in response to LPS. Endotoxin-treated astrocytes provide an alternative anti-inflammatory adaptation, which makes cells less sensitive to acute LPS stimulation than the IL-4 induced adaptation. Taken together, the data reveal that oxylipin profiles associate with different states of polarization to generate a pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory phenotype. This association manifests itself both in native cells and in their responses to a pro-inflammatory stimulus.
Keywords: IL-10; LPS; eicosanoids; endotoxin tolerance; inflammation; interleukins IL-4; oxylipins; polarization; rat astrocytes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
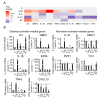
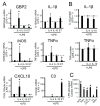
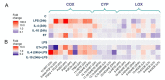
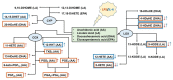
Similar articles
-
Inhibitor of Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis 4-Methylumbelliferone as an Anti-Inflammatory Modulator of LPS-Mediated Astrocyte Responses.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 2;21(21):8203. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218203. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33147798 Free PMC article.
-
High and Low Molecular Weight Hyaluronic Acid Differentially Influences Oxylipins Synthesis in Course of Neuroinflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 9;20(16):3894. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163894. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31405034 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Model of Endotoxin Tolerance in Astrocytes: Role of Interleukin 10 and Oxylipins.Cells. 2019 Dec 1;8(12):1553. doi: 10.3390/cells8121553. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31805746 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of omega-3 fatty acid supplementation on the pattern of oxylipins: a short review about the modulation of hydroxy-, dihydroxy-, and epoxy-fatty acids.Food Funct. 2017 Jul 19;8(7):2355-2367. doi: 10.1039/c7fo00403f. Food Funct. 2017. PMID: 28682409 Review.
-
Interaction of Microglia and Astrocytes in the Neurovascular Unit.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 8;11:1024. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01024. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32733433 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ATP Alters the Oxylipin Profiles in Astrocytes: Modulation by High Glucose and Metformin.Brain Sci. 2025 Mar 11;15(3):293. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15030293. Brain Sci. 2025. PMID: 40149814 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Oxylipins in the Inflammatory-Related Diseases NAFLD, Obesity, and Type 2 Diabetes.Metabolites. 2022 Dec 9;12(12):1238. doi: 10.3390/metabo12121238. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36557276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of PPAR Ligands as Modulators of Resolution of Inflammation, via Their Influence on Cytokines and Oxylipins Release in Astrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 16;21(24):9577. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249577. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33339154 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Dose Dietary Fish Oil Improves RBC Deformability without Improving Post-Transfusion Recovery in Mice.Nutrients. 2023 Oct 20;15(20):4456. doi: 10.3390/nu15204456. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37892532 Free PMC article.
-
ARGEOS: A New Bioinformatic Tool for Detailed Systematics Search in GEO and ArrayExpress.Biology (Basel). 2021 Oct 11;10(10):1026. doi: 10.3390/biology10101026. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34681124 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

