Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Aromatic Amide-Substituted Benzimidazole-Derived Chalcones. The Effect of Upregulating TP53 Protein Expression
- PMID: 32150865
- PMCID: PMC7179225
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25051162
Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Aromatic Amide-Substituted Benzimidazole-Derived Chalcones. The Effect of Upregulating TP53 Protein Expression
Abstract
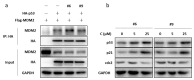
A series of benzimidazole-derived chalcones containing aromatic amide substituent were designed and synthesized. All of the chalcone compounds were tested for their in vitro antitumor activity against human cancer cell lines (HCT116, HepG2, A549, and CRL-5908). The antiproliferative activity of compounds 3, 6, 9, 14, 15, 16 against HCT116 cells was significantly better than that that of 5-Fluorouracil (IC50: 94.63 µM). The antitumor activity of these compounds showed obvious differences between the wild type HCT116 and mutant HCT116 (TP53-/-) cells. A preliminary mechanistic study suggested that these compounds act by upregulating the expression of TP53 protein in tumor cells without inhibiting the MDM2-TP53 interaction.
Keywords: TP53 protein; antiproliferative activities; aromatic amide-substituted; chalcones; upregulating.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 21907010/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 21402012/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 201801D221082/Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province
- 201901D211465/Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province
- 2019L0913/Scientific and Technologial Innovation Programs of Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

