The Complex Network between MYC Oncogene and microRNAs in Gastric Cancer: An Overview
- PMID: 32150871
- PMCID: PMC7084225
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21051782
The Complex Network between MYC Oncogene and microRNAs in Gastric Cancer: An Overview
Abstract
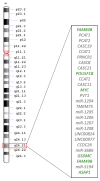
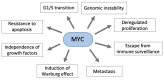
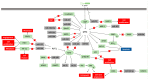
Despite the advancements in cancer treatments, gastric cancer is still one of the leading causes of death worldwide. In this context, it is of great interest to discover new and more effective ways of treating this disease. Accumulated evidences have demonstrated the amplification of 8q24.21 region in gastric tumors. Furthermore, this is the region where the widely known MYC oncogene and different microRNAs are located. MYC deregulation is key in tumorigenesis in various types of tissues, once it is associated with cell proliferation, survival, and drug resistance. microRNAs are a class of noncoding RNAs that negatively regulate the protein translation, and which deregulation is related with gastric cancer development. However, little is understood about the interactions between microRNAs and MYC. Here, we overview the MYC role and its relationship with the microRNAs network in gastric cancer aiming to identify potential targets useful to be used in clinic, not only as biomarkers, but also as molecules for development of promising therapies.
Keywords: 8q24.21; MYC; gastric cancer; microRNA; target therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 201567/2009-1/Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
- 303871/2014-8/Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico
- 2016/25562-0/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 2012/14768-5/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
- 2016/19953-6/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

