Posaconazole Alone and in Combination with Caspofungin for Treatment of Experimental Exserohilum rostratum Meningoencephalitis: Developing New Strategies for Treatment of Phaeohyphomycosis of the Central Nervous System
- PMID: 32150900
- PMCID: PMC7151063
- DOI: 10.3390/jof6010033
Posaconazole Alone and in Combination with Caspofungin for Treatment of Experimental Exserohilum rostratum Meningoencephalitis: Developing New Strategies for Treatment of Phaeohyphomycosis of the Central Nervous System
Abstract
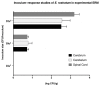
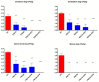
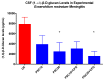
Phaeohyphomycosis of the central nervous system (CNS) is a life-threatening infection associated with severe morbidity. New approaches to treatment of CNS phaeohyphomycosis are critically needed. We therefore studied posaconazole with or without caspofungin for treatment of experimental CNS phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exserohilum rostratum. Each clinical isolate of E. rostratum isolate was inoculated intracisternally with 1.0 × 106 microconidia to fully anesthetized New Zealand White rabbits. Profound persistent neutropenia and immunosuppression were established and maintained using cytarabine and methylprednisolone, respectively. Study groups consisted of posaconazole suspension administered as oral formulation at 10 (PSC10) or 20 (PSC20) mg/kg, caspofungin (CFG) at 2 mg/kg intravenously (IV), combinations of PSC10+CFG or PSC20+CFG, and untreated controls (UC). Posaconazole produced a significant reduction of residual fungal burden of E. rostratum in cerebrum, cerebellum, spinal cord, and paravertebral muscle (p < 0.01), in comparison to UC. The combination of PSC10+CFG and PSC20+CFG achieved full clearance of residual fungal burden from cerebrum, while only PSC20+CFG treated rabbits demonstrated clearance from cerebellum, spinal cord, and paravertebral muscle (p < 0.01). These data correlated with the significant reduction of CSF (1→3)-β-d-glucan levels in rabbits treated with PSC20 and PSC20+CFG in comparison to those of UC (p < 0.05). Posaconazole alone or in combination with caspofungin demonstrated significant antifungal efficacy in the treatment of experimental E. rostratum meningoencephalitis and warrants further study for treatment of CNS phaeohyphomycosis.
Keywords: experimental Exserohilum rostratum meningoencephalitis; posaconazole and caspofungin combination; rabbits.
Conflict of interest statement
Walsh has received grants for experimental and clinical antimicrobial pharmacology and therapeutics to his institution from Allergan, Amplyx, Astellas, Leadiant, Medicines Company, Merck, Scynexis, and Tetraphase and has served as consultant to Amplyx, Astellas, Allergan, ContraFect, Gilead, Leadiant, Medicines Company, Merck, Methylgene, Pfizer, and Scynexis. The other authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antifungal efficacy of isavuconazole and liposomal amphotericin B in a rabbit model of Exserohilum rostratum meningoencephalitis: A preclinical paradigm for management of CNS phaeohyphomycosis.Med Mycol. 2021 Feb 4;59(2):189-196. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myaa102. Med Mycol. 2021. PMID: 33313821 Free PMC article.
-
Sinusitis caused by Exserohilum rostratum after cord blood transplantation for myelodysplastic syndrome: A case report and literature review.Transpl Infect Dis. 2018 Feb;20(1). doi: 10.1111/tid.12805. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Transpl Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 29119669 Review.
-
Cutaneous and subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis caused by Exserohilum rostratum.J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993 Feb;28(2 Pt 2):340-4. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(93)70050-4. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1993. PMID: 8436654
-
Efficacy of caspofungin and posaconazole in a murine model of disseminated Exophiala infection.Med Mycol. 2007 Dec;45(8):685-9. doi: 10.1080/13693780701390157. Med Mycol. 2007. PMID: 17885951
-
Exserohilum rostratum, a rare cause of opportunistic skin infection in children: Case report and review of the literature.Pediatr Dermatol. 2020 Sep;37(5):918-921. doi: 10.1111/pde.14282. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Pediatr Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32677071 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of Novel Thiazole Derivatives Bearing β-Amino Acid and Aromatic Moieties as Promising Scaffolds for the Development of New Antibacterial and Antifungal Candidates Targeting Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens.Molecules. 2021 Dec 23;27(1):74. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010074. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 35011308 Free PMC article.
-
An update on the global treatment of invasive fungal infections.Future Microbiol. 2023 Nov;18(15):1095-1117. doi: 10.2217/fmb-2022-0269. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Future Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37750748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and Pharmacokinetics of Fosmanogepix (APX001) in the Treatment of Candida Endophthalmitis and Hematogenous Meningoencephalitis in Nonneutropenic Rabbits.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021 Feb 17;65(3):e01795-20. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01795-20. Print 2021 Feb 17. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33361304 Free PMC article.
-
Antifungal efficacy of isavuconazole and liposomal amphotericin B in a rabbit model of Exserohilum rostratum meningoencephalitis: A preclinical paradigm for management of CNS phaeohyphomycosis.Med Mycol. 2021 Feb 4;59(2):189-196. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myaa102. Med Mycol. 2021. PMID: 33313821 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

