Synthesis of Tetrabenazine and Its Derivatives, Pursuing Efficiency and Selectivity
- PMID: 32151010
- PMCID: PMC7179236
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25051175
Synthesis of Tetrabenazine and Its Derivatives, Pursuing Efficiency and Selectivity
Abstract
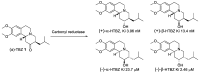
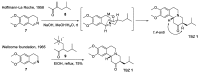
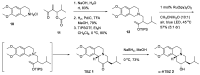
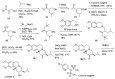
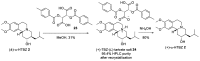
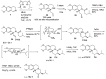
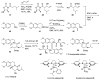
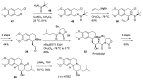
Tetrabenazine is a US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drug that exhibits a dopamine depleting effect and is used for the treatment of chorea in Huntington's disease. Mechanistically, tetrabenazine binds and inhibits vesicular monoamine transporter type 2, which is responsible for importing neurotransmitters from the cytosol to the vesicles in neuronal cells. This transportation contributes to the release of neurotransmitters inside the cell to the synaptic cleft, resulting in dopaminergic signal transmission. The highly potent inhibitory activity of tetrabenazine has led to its advanced applications and in-depth investigation of prodrug design and metabolite drug discovery. In addition, the synthesis of enantiomerically pure tetrabenazine has been pursued. After a series of research studies, tetrabenazine derivatives such as valbenazine and deutetrabenazine have been approved by the US FDA. In addition, radioisotopically labeled tetrabenazine permits the early diagnosis of Parkinson's disease, which is difficult to treat during the later stages of this disease. These applications were made possible by the synthetic efforts aimed toward the efficient and asymmetric synthesis of tetrabenazine. In this review, various syntheses of tetrabenazine and its derivatives have been summarized.
Keywords: Huntington’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; dopamine; tetrabenazine; vesicular monoamine transporter type 2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
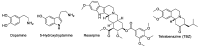

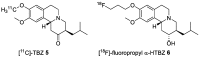
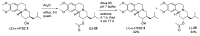


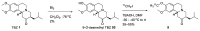

Similar articles
-
Review of deutetrabenazine: a novel treatment for chorea associated with Huntington's disease.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Feb 15;12:313-319. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S138828. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 29497277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deutetrabenazine for tardive dyskinesia and chorea associated with Huntington's disease: a review of clinical trial data.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2019 Dec;20(18):2209-2221. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2019.1674281. Epub 2019 Oct 15. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31613641 Review.
-
A concise total synthesis of (+)-tetrabenazine and (+)-α-dihydrotetrabenazine.Chemistry. 2010 Apr 19;16(15):4623-8. doi: 10.1002/chem.200902591. Epub 2010 Mar 16. Chemistry. 2010. PMID: 20235241
-
Tardive dyskinesia: placing vesicular monoamine transporter type 2 (VMAT2) inhibitors into clinical perspective.Expert Rev Neurother. 2018 Apr;18(4):323-332. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2018.1455504. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Expert Rev Neurother. 2018. PMID: 29557243 Review.
-
Deutetrabenazine: A Review in Chorea Associated with Huntington's Disease.Drugs. 2017 Nov;77(17):1857-1864. doi: 10.1007/s40265-017-0831-0. Drugs. 2017. PMID: 29080203 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug inhibition and substrate transport mechanisms of human VMAT2.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 2;16(1):323. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55361-0. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39747030 Free PMC article.
-
Application of separation and configuration identification of the four tetrabenazine stereoisomers in determining their pharmacokinetics.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025 May;417(11):2253-2266. doi: 10.1007/s00216-025-05813-3. Epub 2025 Mar 8. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40055199
References
-
- Lohr K.M., Bernstein A.I., Stout K., Dunn A., Lazo C.R., Alter S.P., Wang M., Li Y., Fan X., Hess E.J., et al. Increased vesicular monoamine transporter enhances dopamine release and opposes Parkinson disease-related neurodegeneration in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:9977–9982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1402134111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huntington Study Group Tetrabenazine as Antichorea Therapy in Huntington Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Neurology. 2006;66:3663–3672. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

