Extraction and identification of synovial tissue-derived exosomes by different separation techniques
- PMID: 32151262
- PMCID: PMC7063768
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-020-01604-x
Extraction and identification of synovial tissue-derived exosomes by different separation techniques
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study is to compare the efficiency of different separation techniques for extracting synovial tissue-derived exosomes.
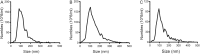
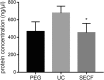
Methods: The synovial tissue discarded during knee arthroscopy or total knee arthroplasty surgery was collected from the Third Affiliated Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine. Ultracentrifugation (UC), filtration combined with size exclusion chromatography (SECF), and 8% polyethylene glycol (PEG) were used to extract synovial tissue-derived exosomes. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), nanoparticle tracer analysis (NTA), and Western Blot (WB) were used to detect the morphology, particle size, and biomarker proteins (CD9, CD63, Flotillin-1, and calnexin) of exosomes.
Results: The extracts of enriched round and discoid vesicles were successfully extracted with UC, SECF, and PEG. The results of TEM have shown that all three extraction methods can extract circular or elliptical vesicles with disc- and cup-shaped structures from the synovial tissue, with the diameter is about 30-150 nm. NTA suggested the main peaks of three groups of exosomes are around 100-120 nm, and the concentration of the three groups of exosomes was greater than 1 × 1010/ml. The results of WB showed that three positive protein markers (CD9, CD63, and Flotillin-1) were highly expressed in the suspension extracted by the three methods and low in the synovial tissue. However, the negative protein (calnexin) was highly expressed in synovial tissues and PEG group, while low in UC and SECF group.
Conclusion: Morphology, particle size, and labeled protein marker detection confirmed that UC, SECF, and PEG can extract exosomes derived from synovial tissue; UC and SECF are more recommended for the extraction of synovial tissue-derived exosomes, which provides a methodological basis for studying the function and mechanism of synovial tissue exosomes in the future.
Keywords: Exosomes; Extracellular vesicles; Osteoarthritis; Synovial tissues.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
How to process synovial fluid samples of gouty arthritis and extract its exosomes for subsequent cytokine analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Aug 4;102(31):e34552. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034552. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37543776 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome enrichment by ultracentrifugation and size exclusion chromatography.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018 Jan 1;23(5):865-874. doi: 10.2741/4621. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018. PMID: 28930577
-
A Comparative Study of Serum Exosome Isolation Using Differential Ultracentrifugation and Three Commercial Reagents.PLoS One. 2017 Jan 23;12(1):e0170628. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170628. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28114422 Free PMC article.
-
Methods of isolating extracellular vesicles impact down-stream analyses of their cargoes.Methods. 2015 Oct 1;87:3-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.02.019. Epub 2015 Mar 10. Methods. 2015. PMID: 25766927 Review.
-
A review on separation and application of plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles.J Sep Sci. 2024 Apr;47(8):e2300669. doi: 10.1002/jssc.202300669. J Sep Sci. 2024. PMID: 38651549 Review.
Cited by
-
Adenosine and Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Are Present in Blood Serum and Exosomes from SAMP8 Mice: Modulation by Aging and Resveratrol.Cells. 2020 Jul 7;9(7):1628. doi: 10.3390/cells9071628. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32645849 Free PMC article.
-
Microneedle loaded with luteolin-colostrum-derived exosomes: a dropless approach for treatment of glaucoma.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Jul 11. doi: 10.1007/s13346-025-01914-9. Online ahead of print. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40643885
-
Changes in phospholipid metabolism in exosomes of hormone-sensitive and hormone-resistant prostate cancer cells.J Cancer. 2021 Mar 15;12(10):2893-2902. doi: 10.7150/jca.48906. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33854590 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Exosomal Isolation Methods: Is Size Exclusion Chromatography the Best Option?Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 4;21(18):6466. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186466. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32899828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Information Transfer and Biological Significance of Neoplastic Exosomes in the Tumor Microenvironment of Osteosarcoma.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Sep 8;13:8931-8940. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S266835. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32982285 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

