Supporting antidepressant discontinuation: the development and optimisation of a digital intervention for patients in UK primary care using a theory, evidence and person-based approach
- PMID: 32152159
- PMCID: PMC7064123
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-032312
Supporting antidepressant discontinuation: the development and optimisation of a digital intervention for patients in UK primary care using a theory, evidence and person-based approach
Abstract
Objectives: We aimed to develop a digital intervention to support antidepressant discontinuation in UK primary care that is scalable, accessible, safe and feasible. In this paper, we describe the development using a theory, evidence and person-based approach.
Design: Intervention development using a theory, evidence and person-based approach.
Setting: Primary Care in the South of England.
Participants: Fifteen participants with a range of antidepressant experience took part in 'think aloud' interviews for intervention optimisation.
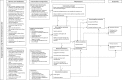
Intervention: Our digital intervention prototype (called 'ADvisor') was developed on the basis of a planning phase consisting of qualitative and quantitative reviews, an in-depth qualitative study, the development of guiding principles and a theory-based behavioural analysis. Our optimisation phase consisted of 'think aloud' interviews where the intervention was iteratively refined.
Results: The qualitative systematic review and in-depth qualitative study highlighted the centrality of fear of depression relapse as a key barrier to discontinuation. The quantitative systematic review showed that psychologically informed approaches such as cognitive-behavioural therapy were associated with greater rates of discontinuation than simple advice to reduce. Following a behavioural diagnosis based on the behaviour change wheel, social cognitive theory provided a theoretical basis for the intervention. The intervention was optimised on the basis of think aloud interviews, where participants suggested they like the flexibility of the system and found it reassuring. Changes were made to the tone of the material and the structure was adjusted based on this qualitative feedback.
Conclusions: 'ADvisor' is a theory, evidence and person-based digital intervention designed to support antidepressant discontinuation. The intervention was perceived as helpful and reassuring in optimisation interviews. Trials are now needed to determine the feasibility, clinical and cost-effectiveness of this approach.
Keywords: antidepressants; depression & mood disorders; digital intervention; intervention development; primary care.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: TK reports grants from National Institute for Health Research, during the conduct of the study. JM reports grants from National Institute of Health Research, during the conduct of the study; and is a member of the Council for Evidence-based Psychiatry which is an unfunded organisation, whose mission is to 'communicate evidence of the potentially harmful effects of psychiatric drugs to the people and institutions in the UK that can make a difference'.
Figures
References
-
- Health and Social Care Information Centre Prescriptions Dispensed in the Community - Statistics for England 2006-2016, 2017. Available: https://digital.nhs.uk/data-and-information/publications/statistical/pre... [Accessed 2 Jul 2018].
-
- OECD Health at a glance: Europe, 2012.
-
- Scholes S, Faulding S, Mindell J. Use of prescribed medicines In: Health and social care information centre, 2014. https://files.digital.nhs.uk/publicationimport/pub16xxx/pub16076/hse2013...