Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas: Malignancies Arising from Mature B Cells
- PMID: 32152246
- PMCID: PMC7919396
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a034843
Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas: Malignancies Arising from Mature B Cells
Abstract
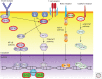
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) are a diverse group of entities, both clinically and molecularly. Here, we review the evolution of classification schemes in B-cell lymphoma, noting the now standard WHO classification system that is based on immune cell-of-origin and molecular phenotypes. We review how lymphomas arise throughout the B-cell development process as well as the molecular and clinical features of prominent B-cell lymphomas. We provide an overview of the major progress that has occurred over the past decade in terms of our molecular understanding of these diseases. We discuss treatment options available and focus on a number of the diverse research tools that have been employed to improve our understanding of these diseases. We discuss the problem of heterogeneity in lymphomas and anticipate that the near future will bring significant advances that provide a measurable impact on NHL outcomes.
Copyright © 2021 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Bacac M, Colombetti S, Herter S, Sam J, Perro M, Chen S, Bianchi R, Richard M, Schoenle A, Nicolini V, et al. 2018. CD20-TCB with obinutuzumab pretreatment as next-generation treatment of hematologic malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 24: 4785–4797. - PubMed
-
- Béguelin W, Teater M, Gearhart MD, Calvo Fernández MT, Goldstein RL, Cárdenas MG, Hatzi K, Rosen M, Shen H, Corcoran CM, et al. 2016. EZH2 and BCL6 cooperate to assemble CBX8-BCOR complex to repress bivalent promoters, mediate germinal center formation and lymphomagenesis. Cancer Cell 30: 197–213. 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.07.006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
