Modified Synthesis of the Peptidomimetic Natriuretic Peptide Receptor-C Antagonist M372049
- PMID: 32153307
- PMCID: PMC7062365
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2020.151654
Modified Synthesis of the Peptidomimetic Natriuretic Peptide Receptor-C Antagonist M372049
Abstract
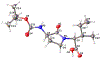
The Natriuretic Peptide Receptors (NPRs) regulate vascular sodium levels and have been of significant interest for the potential treatment of hypertension and related cardiovascular complications. The peptidomimetic antagonist M372049 is a valuable probe for the study of NPR-C signaling, unfortunately it is presently not commercially available. Described is a detailed protocol for its synthesis that does not require specialized apparatus and builds upon a prior patent from Veale and colleagues. Key steps include a base-mediated lactam formation and a solid-supported peptide synthetic sequence. An X-ray crystal structure of a key lactam intermediate was obtained to confirm the structure and relative stereochemistry of the compound.
Keywords: M372049; NPR-C antagonist; Natriuretic Peptide Receptor-C; lactam; peptide synthesis; peptidomimetic.
Figures
References
-
- LaDisa JF; Tomita-Mitchell A; Stamm K; Bazan K; Mahnke DK; Goetsch MA; Wegter BJ; Gerringer JW; Repp K; Palygin O; Zietara AP; Krolikowski MM; Eddinger TJ; Alli AA; Mitchell ME. Human Genotyping and an Experimental Model Reveal NPR-C as a Possible Contributor to Morbidity in Coarctation of the Aorta. Physiol. Genomics 2019, 51 (6), 177–185. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anand-Srivastava MB; Franks DJ; Cantin M; Genest J. Atrial Natriuretic Factor Inhibits Adenylate Cyclase Activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 1984, 121 (3), 855–862. - PubMed
-
- Maack T; Suzuki M; Almeida FA; Nussenzveig D; Scarborough RM; McEnroe GA; Lewicki JA. Physiological Role of Silent Receptors of Atrial Natriuretic Factor. Science 1987, 238 (4827), 675–678. - PubMed
-
- Veale CA; Alford VC; Aharony D; Banville DL; Bialecki RA; Brown FJ; Damewood JR; Dantzman CL; Edwards PD; Jacobs RT; Mauger RC; Murphy MM; Palmer W; Pine KK; Rumsey WL; Garcia-Davenport LE; Shaw A; Steelman GB; Surian JM; Vacek EP. The Discovery of Non-Basic Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Clearance Receptor Antagonists. Part 1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2000, 10 (17), 1949–1952. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources