Rare Variants in Genes Linked to Appetite Control and Hypothalamic Development in Early-Onset Severe Obesity
- PMID: 32153512
- PMCID: PMC7047210
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00081
Rare Variants in Genes Linked to Appetite Control and Hypothalamic Development in Early-Onset Severe Obesity
Abstract
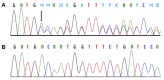
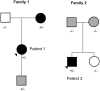
Context: The hypothalamic circuit has an essential role in the regulation of appetite and energy expenditure. Pathogenic variants in genes involved in the hypothalamic leptin-melanocortin pathway, including melanocortin-4-receptor (MC4R), have been associated with monogenic obesity. Objective: To determine the rate and spectrum of rare variants in genes involved in melanocortin pathway or hypothalamic development in patients with severe early-onset obesity (height-adjusted weight >60% before age 10 years). Methods: We used a custom-made targeted exome sequencing panel to assess peripheral blood DNA samples for rare (minor allele frequency <0.5%), pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants in 24 genes related to the hypothalamic circuit in 92 subjects (51% males, median age 13.7 years) with early-onset severe obesity (median body mass index (BMI) Z-score + 4.0). Results: We identified a novel frameshift deletion in MC4R (p.V103Afs5*) in two unrelated patients and a previously reported MC4R variant (p.T112M) in one patient. In addition, we identified rare heterozygous missense variants in ADCY3 (p.G1110R), MYT1L (p.R807Q), ISL1 (p.I347F), LRP2 (p.R2479I, and p.N3315S) and a hemizygous missense variant in GRPR (p.L87M) (each in one patient), possibly contributing to the obesity phenotype in these patients. Altogether 8 % (7/92) of the subjects had rare pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants in the studied genes. Conclusions: Rare genetic variants within the hypothalamic circuit are prevalent and contribute to the development of severe early-onset obesity. Targeted exome sequencing is useful in identifying affected subjects. Further studies are needed to evaluate the variants' clinical significance and to define optimal treatment.
Keywords: MC4R; appetite regulation; childhood obesity; hyperphagia; hypothalamus.
Copyright © 2020 Loid, Mustila, Mäkitie, Viljakainen, Kämpe, Tossavainen, Lipsanen-Nyman, Pekkinen and Mäkitie.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

