Baseline diet quality of predominantly minority children and adolescents from households characterized by low socioeconomic status in the Childhood Obesity Prevention and Treatment Research (COPTR) Consortium
- PMID: 32153951
- PMCID: PMC7050800
- DOI: 10.1186/s40795-019-0302-y
Baseline diet quality of predominantly minority children and adolescents from households characterized by low socioeconomic status in the Childhood Obesity Prevention and Treatment Research (COPTR) Consortium
Abstract
Background: The Healthy Eating Index (HEI-2010) is a measure of diet quality that examines conformance with the Dietary Guidelines for Americans. The objectives of this study were to estimate baseline diet quality of predominantly low-income minority children using the HEI-2010 and to identify the most important HEI components to target for dietary intervention.
Methods: Two or three baseline 24 h dietary recalls were collected in-person or over telephone between May 2012 and June 2014 from 1,745 children and adolescents from four randomized clinical trials in the Childhood Obesity Prevention and Treatment Research (COPTR) Consortium. Nine adequacy and three moderation food components were calculated and averaged to determine overall HEI scores. The overall HEI-2010 scores were categorized as ≥81, 51-80, or ≤ 50 based on the HEI-2005 classification. For each study, mean overall and component HEI scores were estimated using linear regression models.
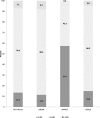
Results: Mean (95% CI) overall HEI scores ranged from 47.9 (46.8, 49.0) to 64.5 (63.6, 65.4). Only 0.3 to 8.1% of children and adolescents had HEI-2010 score ≥ 81. The average component score for green and beans was less than 30% of maximum score for all trials. In contrast, the average component score for protein, dairy (except for IMPACT), and empty calories (except forIMPACT) was more than 80% of maximum score.
Conclusions: Based on HEI-2010 scores, few children and adolescents consumed high quality diets. Dietary interventions for children and adolescents should focus on improving intakes of green vegetables and beans.
Clinical trial registry numbers: GROW study (clinical trial # NCT01316653); NET-Works study (clinical trial #NCT01606891); Stanford Goals (clinical trial #NCT01642836); IMPACT (clinical trial # NCT01514279).
Keywords: Body mass index; Children; Diet quality; Obesity.
© The Author(s). 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests. None of the authors reported any financial conflicts of interest related to the present article.
Figures

References
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
