Tumor Contrast-Enhancement for Monitoring of PRRT 177Lu-DOTATATE in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor Patients
- PMID: 32154181
- PMCID: PMC7047407
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00193
Tumor Contrast-Enhancement for Monitoring of PRRT 177Lu-DOTATATE in Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor Patients
Abstract
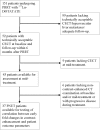
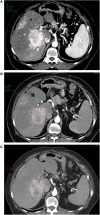
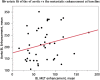
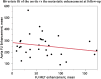
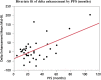
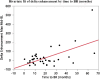
Background: Therapy monitoring of cancer treatment by contrast-enhanced CT (CECT), applying response evaluation criteria in solid tumors criteria version 1. 1 (RECIST 1.1) is less suitable for neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) which, when responding, tend to show stabilization rather than shrinkage. New methods are needed to further classify patients in order to identify non-responders at an early stage and avoid unnecessary adverse effects and costs. Changes in arterial tumor attenuation and contrast-enhancement could be used to identify the effect of therapy, perhaps even in early stages of treatment. Methods: Patients with metastatic pancreatic NETs (PNETs) receiving peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) with 177Lu-DOTATATE underwent CECT at baseline, mid-treatment (PRRT cycles 3-5) and at follow-up, 3 months after the last PRRT cycle. At baseline CECT, the liver metastasis with the highest arterial attenuation was identified in each patient. The fold changes in arterial tumor attenuation (Hounsfield Units, HU), contrast-enhancement (HU), and transversal tumor area (cm2) between CECT at baseline, mid-treatment and follow-up were calculated. Correlation of the tumor metrics to outcome parameters such as progression-free survival (PFS) and time to best response was performed. Results: Fifty-two patients were included (27 men, 25 women), median age 60 years (range 29-80), median Ki-67 8% (range 1-30). Six patients had grade 1 PNETs, forty had grade 2 and four had grade 3 tumors. As an internal control, it was first tested and established that the tumor contrast-enhancement was not merely related to that of the abdominal aorta. The mean ± SD arterial attenuation of the liver metastases was similar at baseline, 217 ± 62 HU and at mid-treatment, 238 ± 80 HU and then decreased to 198 ± 62 HU at follow-up, compared to baseline (p = 0.024, n = 52) and mid-treatment (p = 0.0004, n = 43). The transversal tumor area decreased 25% between baseline and follow-up (p = 0.013, n = 52). Tumor contrast-enhancement increased slightly from baseline to mid-treatment and these fold changes correlated with PFS (R 2 = 0.33, p = 0.0002, n = 37) and with time to best response (R 2 = 0.34, p < 0.0001, n = 37). Conclusions: Early changes in contrast-enhancement and arterial attenuation in PNET liver metastases may for CECT monitoring of PRRT yield complementary information to evaluation by RECIST 1.1.
Keywords: 177Lu; CT; NET; PRRT; computed tomography; contrast-enhancement; neuroendocrine tumor; therapy monitoring.
Copyright © 2020 Pettersson, Fröss-Baron, Crona and Sundin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical Response Profile of Metastatic/Advanced Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumors to Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy with 177Lu-DOTATATE.Clin Nucl Med. 2017 Jun;42(6):428-435. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000001639. Clin Nucl Med. 2017. PMID: 28319500
-
Prevalence of hitherto unknown brain meningioma detected on 68Ga-DOTATATE positron-emission tomography/computed tomography in patients with metastatic neuroendocrine tumor and exploring potential of 177Lu-DOTATATE peptide receptor radionuclide therapy as single-shot treatment approach targeting both tumors.World J Nucl Med. 2019 Apr-Jun;18(2):160-170. doi: 10.4103/wjnm.WJNM_39_18. World J Nucl Med. 2019. PMID: 31040748 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Choi, RECIST and Somatostatin Receptor PET/CT Based Criteria for the Evaluation of Response and Response Prediction to PRRT.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 16;14(6):1278. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14061278. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35745849 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy for Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumours.Curr Radiopharm. 2019;12(2):126-134. doi: 10.2174/1874471012666190201164132. Curr Radiopharm. 2019. PMID: 30714538 Review.
-
Everolimus, lutetium-177 DOTATATE and sunitinib for advanced, unresectable or metastatic neuroendocrine tumours with disease progression: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2018 Sep;22(49):1-326. doi: 10.3310/hta22490. Health Technol Assess. 2018. PMID: 30209002 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) with 177Lu-DOTATATE; Differences in Tumor Dosimetry, Vascularity and Lesion Metrics in Pancreatic and Small Intestinal Neuroendocrine Neoplasms.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 25;13(5):962. doi: 10.3390/cancers13050962. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668887 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship Between Best Tumor Shrinkage and Progression-Free Survival and Overall Survival in Patients With Progressive Midgut Neuroendocrine Tumors Treated With [177Lu]Lu-DOTA-TATE: Ad Hoc Analysis of the Phase III NETTER-1 Trial.Cancer Med. 2025 May;14(9):e70744. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70744. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40272146 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tumor growth rate in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor patients undergoing PRRT with 177Lu-DOTATATE.Endocr Connect. 2021 Apr 22;10(4):422-431. doi: 10.1530/EC-21-0027. Endocr Connect. 2021. PMID: 33875614 Free PMC article.
-
Radiological and Clinical Efficacy of Intra-Arterial 90Y-DOTATATE in Patients with Unresectable, Progressive, Liver Dominant Neuroendocrine Neoplasms.J Clin Med. 2021 Apr 20;10(8):1794. doi: 10.3390/jcm10081794. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33924160 Free PMC article.
-
The Challenge of Evaluating Response to Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy in Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: The Present and the Future.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Dec 12;10(12):1083. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10121083. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33322819 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

