Comparison of Early vs. Delayed Anakinra Treatment in Patients With Adult Onset Still's Disease and Effect on Clinical and Laboratory Outcomes
- PMID: 32154255
- PMCID: PMC7047849
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00042
Comparison of Early vs. Delayed Anakinra Treatment in Patients With Adult Onset Still's Disease and Effect on Clinical and Laboratory Outcomes
Abstract
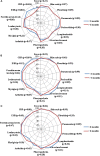
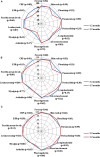
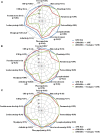
Background: Aim of this study was to search for any difference in the outcome of patients with adult onset Still's disease (AOSD) treated with anakinra (ANK) in relation with the interval between disease onset and the start of anti-interleukin(IL)-1 treatment and according with the different lines of ANK treatment. Patients and Methods: One hundred and forty-one AOSD patients treated with ANK have been retrospectively assessed. Statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) were analyzed in the frequency of ANK effectiveness, primary or secondary inefficacy to ANK and rate of resolution of clinical and laboratory AOSD manifestations after 3, 6, and 12 months since ANK treatment according with different lines of treatment and different times between AOSD onset and start of ANK. Results: No significant differences were identified in the ANK effectiveness and frequency of primary or secondary inefficacy for patients starting ANK within 6 months (p = 0.19, p = 0.14, and p = 0.81, respectively) or 12 months (p = 0.37, p = 0.23, and p = 0.81, respectively) since AOSD onset compared with patients starting ANK thereafter; no significant differences were identified in ANK effectiveness and primary or secondary inefficacy according with different lines of ANK treatment (p = 0.06, p = 0.19, and p = 0.13, respectively). Patients starting ANK within 6 and 12 months since AOSD onset showed a significantly quicker decrease of erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein than observed among patients undergoing ANK treatment after 6 and 12 months. The number of swollen joints at the 3 month follow-up visit was significantly lower among patients undergoing ANK within 6 months since AOSD onset (p = 0.01), while no significance was identified at the 6 and 12 month assessments (p = 0.23 and p = 0.45, respectively). At the 3 and 6 month visits, the number of swollen joints was significantly higher among patients previously treated with conventional and biological disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) compared with those formerly treated only with conventional DMARDs (p < 0.017). Conclusions: Clinical and therapeutic outcomes are substantially independent of how early ANK treatment is started in AOSD patients. However, a faster ANK effectiveness in controlling systemic inflammation and resolving articular manifestations may be observed in patients benefiting from IL-1 inhibition as soon as after disease onset.
Keywords: adult onset Still's disease; anakinra; autoinflammatory diseases; innovative biotechnologies; interleukin-1; personalized medicine; systemic onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis; treat to target.
Copyright © 2020 Vitale, Cavalli, Ruscitti, Sota, Colafrancesco, Priori, Valesini, Argolini, Baldissera, Bartoloni, Cammelli, Canestrari, Cavallaro, Massaro, Cipriani, De Marchi, De Vita, Emmi, Frassi, Gerli, Gremese, Iannone, Fornaro, Paladini, Lopalco, Manna, Mathieu, Montecucco, Mosca, Piazza, Piga, Pontikaki, Romano, Rossi, Rossini, Silvestri, Stagnaro, Talarico, Frediani, Tincani, Viapiana, Vitiello, Galozzi, Sfriso, Gaggiano, Grosso, Rigante, Dagna, Giacomelli and Cantarini.
Figures

References
-
- Uppal SS, Pande IR, Kumar A, Kailash S, Sekharan NG, Adya CM, et al. . Adult onset Still's disease in northern India: comparison with juvenile onset Still's disease. Br J Rheumatol. (1995) 34:429–34. - PubMed
-
- Luthi F, Zufferey P, Hofer MF, So AK. “Adolescent-onset Still's disease”: characteristics and outcome in comparison with adult-onset still's disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2002) 20:427–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

