The Role of Egg Production in the Etiology of Keel Bone Damage in Laying Hens
- PMID: 32154276
- PMCID: PMC7047165
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00081
The Role of Egg Production in the Etiology of Keel Bone Damage in Laying Hens
Abstract
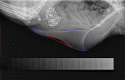
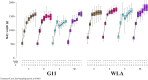
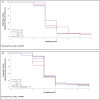
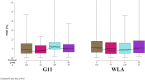
Keel bone fractures and deviations belong to the most severe animal welfare problems in laying hens and are influenced by several factors such as husbandry system and genetic background. It is likely that egg production also influences keel bone health due to the high demand of calcium for the eggshell, which is, in part, taken from the skeleton. The high estrogen plasma concentration, which is linked to the high laying performance, may also affect the keel bone as sexual steroids have been shown to influence bone health. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between egg production, genetically determined high laying performance, estradiol-17ß concentration, and keel bone characteristics. Two hundred hens of two layer lines differing in laying performance (WLA: high performing; G11: low performing) were divided into four treatment groups: Group S received an implant containing a GnRH agonist that suppressed egg production, group E received an implant containing the sexual steroid estradiol-17ß, group SE received both implants, and group C were kept as control hens. Between the 12th and the 62nd weeks of age, the keel bone of all hens was radiographed and estradiol-17ß plasma concentration was assessed at regular intervals. Non-egg laying hens showed a lower risk of keel bone fracture and a higher radiographic density compared to egg laying hens. Exogenous estradiol-17ß was associated with a moderately higher risk of fracture within egg laying but with a lower risk of fracture and a higher radiographic density within non-egg laying hens. The high performing layer line WLA showed a significantly higher fracture risk but also a higher radiographic density compared to the low performing layer line G11. In contrast, neither the risk nor the severity of deviations were unambiguously influenced by egg production or layer line. We assume that within a layer line, there is a strong association between egg production and keel bone fractures, and, possibly, bone mineral density, but not between egg production and deviations. Moreover, our results confirm that genetic background influences fracture prevalence and indicate that the selection for high laying performance may negatively influence keel bone health.
Keywords: deviation; egg production; fracture; hen; keel bone; laying performance; radiographic density.
Copyright © 2020 Eusemann, Patt, Schrader, Weigend, Thöne-Reineke and Petow.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Estradiol-17ß Is Influenced by Age, Housing System, and Laying Performance in Genetically Divergent Laying Hens (Gallus gallus f.d.).Front Physiol. 2022 Jul 22;13:954399. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.954399. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35936910 Free PMC article.
-
Bone quality and composition are influenced by egg production, layer line, and oestradiol-17ß in laying hens.Avian Pathol. 2022 Jun;51(3):267-282. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2022.2050671. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Avian Pathol. 2022. PMID: 35261302
-
Radiographic examination of keel bone damage in living laying hens of different strains kept in two housing systems.PLoS One. 2018 May 9;13(5):e0194974. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194974. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29742164 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Keel Bone Damage on Welfare of Laying Hens.Front Vet Sci. 2018 Feb 28;5:6. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2018.00006. eCollection 2018. Front Vet Sci. 2018. PMID: 29541640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Welfare implications of avian osteoporosis.Poult Sci. 2004 Feb;83(2):184-92. doi: 10.1093/ps/83.2.184. Poult Sci. 2004. PMID: 14979568 Review.
Cited by
-
A tagged visual analog scale is a reliable method to assess keel bone deviations in laying hens from radiographs.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Aug 18;9:937119. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.937119. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36061110 Free PMC article.
-
Keel bone fractures in Danish laying hens: Prevalence and risk factors.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 13;16(8):e0256105. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256105. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34388183 Free PMC article.
-
Comparisons of longitudinal radiographic measures of keel bones, tibiotarsal bones, and pelvic bones versus post-mortem measures of keel bone damage in Bovans Brown laying hens housed in an aviary system.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Sep 30;11:1432665. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1432665. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39403210 Free PMC article.
-
Estradiol-17ß Is Influenced by Age, Housing System, and Laying Performance in Genetically Divergent Laying Hens (Gallus gallus f.d.).Front Physiol. 2022 Jul 22;13:954399. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.954399. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35936910 Free PMC article.
-
Japanese quails (Coturnix Japonica) show keel bone damage during the laying period-a radiography study.Front Physiol. 2024 Mar 6;15:1368382. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1368382. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38545371 Free PMC article.
References
-
- EFSA Welfare aspects of various systems of keeping laying hens. EFSA J. (2005) 197:1–23. 10.2903/j.efsa.2005.197 - DOI
-
- FAWC Opinion on Osteoporosis and Bone Fractures in Laying Hens. London: Farm Animal Welfare Committee; (2010).
-
- FAWC An Open Letter to Great Britain Governtments: Keel Bone Fractures in Laying Hens. London: Farm Animal Welfare Committee; (2013).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

