Protocol for the EARCO Registry: a pan-European observational study in patients with α1-antitrypsin deficiency
- PMID: 32154291
- PMCID: PMC7049712
- DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00181-2019
Protocol for the EARCO Registry: a pan-European observational study in patients with α1-antitrypsin deficiency
Abstract
Rationale and objectives: Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (AATD) is a genetic condition that leads to an increased risk of emphysema and liver disease. Despite extensive investigation, there remain unanswered questions concerning the natural history, pathophysiology, genetics and the prognosis of the lung disease in association with AATD. The European Alpha-1 Clinical Research Collaboration (EARCO) is designed to bring together researchers from European countries and to create a standardised database for the follow-up of patients with AATD.
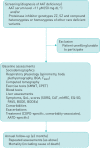
Study design and population: The EARCO Registry is a non-interventional, multicentre, pan-European, longitudinal observational cohort study enrolling patients with AATD. Data will be collected prospectively without interference/modification of patient's management by the study team. The major inclusion criterion is diagnosed severe AATD, defined by an AAT serum level <11 µM (50 mg·dL-1) and/or a proteinase inhibitor genotype ZZ, SZ or compound heterozygotes or homozygotes of other rare deficient variants. Assessments at baseline and during the yearly follow-up visits include lung function testing (spirometry, body plethysmography and diffusing capacity of the lung), exercise capacity, blood tests and questionnaires (symptoms, quality of life and physical activity). To ensure correct data collection, there will be designated investigator staff to document the data in the case report form. All data will be reviewed by the EARCO database manager.
Summary: The EARCO Registry aims to understand the natural history and prognosis of AATD better with the goal to create and validate prognostic tools to support medical decision-making.
Copyright ©ERS 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: T. Greulich reports grants from CSL-Behring, Grifols and Kamda during the conduct of the study; personal fees for lectures and advisory boards from AstraZeneca, Berlin-Chemie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, CSL-Behring, GSK and Novartis, grants and personal fees for lectures and advisory boards from Grifols, and grants from the German Centre for Lung Research (DZL), outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: A. Altraja reports travel support to attend the EARCO stakeholder board meeting on 17 June 2019 from EARCO during the conduct of the study; support for clinical trials and honoraria for advisory board meetings from CSL Behring, honoraria for lectures/chairmanships and advisory board meetings and travel support from Shire Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi (Norameda), GlaxoSmithKline, MSD, Novartis, Roche, Bayer and Actelion (Johnson & Johnson), research support from Pfizer, travel support from Teva, Sanofi and United Therapeutics (AOP Orphan), honoraria for lectures and travel support from Berlin-Chemie Menarini Group, and honoraria for lectures from Orion, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: M. Barrecheguren reports speaker fees from Menarini, Grifols, CSL Behring, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gebro Pharma and GlaxoSmithKline, and consulting fees from Novartis and GlaxoSmithKline, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: R. Bals reports grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim, personal fees from GlaxoSmithKline and Grifols, grants and personal fees from Novartis, personal fees from CSL Behring, grants from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) Competence Network Asthma and COPD (ASCONET), Sander Stiftung, Schwiete Stiftung, Krebshilfe and Mukoviszidose e.V., outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: J. Chlumsky reports personal fees for lectures and consultation from CSL Behring, and travel support from CSL Behring, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: J. Chorostowska-Wynimko reports grants, personal fees and nonfinancial support from Grifols, personal fees from Kamada, grants, personal fees and nonfinancial support from AstraZeneca, personal fees and nonfinancial support from Pfizer, MSD and BMS, personal fees from GSK, Novartis amd Chiesi, personal fees and nonfinancial support from Roche, grants and personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, personal fees and nonfinancial support from Abbvie, grants, personal fees and nonfinancial support from CSL Behring, personal fees from Lekam, grants, personal fees and nonfinancial support from CelonPharma, and personal fees from Takeda, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: C. Clarenbach reports consulting fees and travel support from Vifor Pharma, and consulting or speaker fees from Boehringer, Novartis, GSK, AstraZeneca and Sanofi, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: L. Corda has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A.G. Corsico has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: I. Ferrarotti has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: C. Esquinas has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: C. Gouder has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A. Hećimović reports speaker fees from Roche, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis and MSD, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: A. Ilic has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: Y. Ivanov has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: S. Janciauskiene has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: W. Janssens reports receiving research grants and money for consultancy activities from Behring, AstraZeneca, Boerhinger Ingelheim, GSK, Chiesi, outside the submitted work. He is co-founder of ArtiQ, a spinoff company in healthcare. Conflict of interest: M. Kohler reports advisor fees from Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, GSK and Bayer, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: A. Krams reports personal fees and nonfinancial support from AstraZeneca, Berlin-Chemie/Menarini and Boehringer Ingelheim, personal fees from GlaxoSmithKline and Merck Serono, personal fees and nonfinancial support from Norameda (represents Chiesi in Baltic countries), personal fees from Novartis, and nonfinancial support from Mylan, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: B. Lara has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: R. Mahadeva reports personal fees from Chiesi, Astra Zeneca and Boehringer Ingelheim, and grants from Pfizer Open Air, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: G. McElvaney has sat on advisory boards for CSL Behring, Grifols, Vertex and Chiesi. Conflict of interest: J-F. Mornex reports nonfinancial support from ADAAT, grants, personal fees and nonfinancial support from LFB and CSL Behring, nonfinancial support from Grifols, personal fees and nonfinancial support from Polyphor, during the conduct of the study; personal fees and nonfinancial support from Actelion, GSK, Roche and Novartis, nonfinancial support from Bayer, personal fees and nonfinancial support from BMS, nonfinancial support from Pfizer and MSD, personal fees from Ellivie, and nonfinancial support from Boehringer, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: K. O'Hara reports nonfinancial support from ELF/ERS and Mereo BioPharma Group PLC, grants from CSL Behring, and also receives donations from individuals/companies as a result of fundraising activities; personal fees and nonfinancial support from NICE and nonfinancial support from Alpha-1 Global, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: D. Parr reports advisory board and consultancy fees from CSL Behring and Kamada, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: E. Piitulainen has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: K. Schmid-Scherzer has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: N. Seersholm has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: R.A. Stockley reports a grant for a small, investigator-lead project and personal fees for a trial steering board from CSL Behring; a lecture fee from GSK; advisory board fees from Vertex, inhbrix, Mereobiopharma and Novartis; and lecture fees from Grifols, during the conduct of the study. He acts in an advisory manner for several companies with an interest in α1-antitrypsin deficiency. Conflict of interest: J. Stolk has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Sucena reports lecture fees and travel pay from Grifols and CSL Behring, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: H. Tanash has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A. Turner reports grants and personal fees from CSL Behring; personal fees and nonfinancial support from Boehringer Ingelheim; nonfinancial support from GSK; grants, personal fees and nonfinancial support from AstraZeneca; grants, personal fees and nonfinancial support from Chiesi; grants from Grifols biotherapeutics, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: R. Ulmeanu has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Wilkens reports that as chairman of the patient organisation Alpha1 Deutschland e.V., he does not receive personally any donations but his organisation receives money from public funds as well as from the pharmaceutical industry, including grants and travelling costs. Conflict of interest: A. Yorgancıoğlu reports grants from MSD, and personal fees from GSK, AstraZeneca, Abdi Ibrahim, Chiesi, Novartis and Sandoz, outside the submitted work. Conflict of interest: A. Zaharie has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Miravitlles reports speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, Cipla, AstraZeneca, Menarini, Rovi, Bial, Zambon, CSL Behring, Grifols and Novartis, consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Bial, Gebro Pharma, CSL Behring, Laboratorios Esteve, Ferrer, Mereo Biopharma, Verona Pharma, TEVA, pH Pharma, Novartis and Grifols, and research grants to his institution from GlaxoSmithKline and Grifols, outside the submitted work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
