Evaluating the effectiveness of integrating radiological and cross-sectional anatomy in first-year medical students - A randomized, crossover study
- PMID: 32154311
- PMCID: PMC7034166
- DOI: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_325_19
Evaluating the effectiveness of integrating radiological and cross-sectional anatomy in first-year medical students - A randomized, crossover study
Abstract
Context: Radiological anatomy (RA) knowledge is essential for the current-day clinical practice due to the rapid development in imaging technologies. As there is a long interval between learning RA in the 1st year and applying it in their clinical disciplines impedes their functional understanding, this study has been planned to provide the students with a right mix of anatomy and radiology in order to promulgate deeper medical comprehension.
Aim: This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of integrated RA in honing the radiological reasoning abilities in 1st year medical students and to develop critical thinking skills through small-group, case-based learning experience.
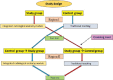
Methodology: All the students of 2017-2018 batch were randomized equally into study group and control group. The study group was exposed to the interactive RA module followed by posttest. The control group was exposed to traditional teaching and then given posttest. The groups were flipped for successive regions of anatomy. Feedbacks were obtained by both quantitative and qualitative methods.
Statistical analysis: Posttest scores were compared using Student's t-test. Feedbacks were analyzed using descriptive statistics.
Results: The posttest scores were significantly higher in the study group when compared to the control group. Nearly 92% of the students felt that the integrated module made them learn better and 44% of the students felt that it helped them to apply the knowledge in clinical context.
Conclusion: For the present millennial-generation students, integrated RA lectures help develop their critical thinking and help in the subsequent clinical years.
Keywords: Cross-sectional anatomy; integrated radiology; radiological anatomy module.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Education and Health Promotion.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Infusing the axioms of clinical reasoning while designing clinical anatomy case vignettes teaching for novice medical students: a randomised cross over study.Anat Cell Biol. 2020 Jun 30;53(2):151-161. doi: 10.5115/acb.19.199. Anat Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32647083 Free PMC article.
-
The Benefits of an Augmented Reality Magic Mirror System for Integrated Radiology Teaching in Gross Anatomy.Anat Sci Educ. 2019 Nov;12(6):585-598. doi: 10.1002/ase.1864. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Anat Sci Educ. 2019. PMID: 30697948 Free PMC article.
-
Interactive radiological anatomy eLearning solution for first year medical students: Development, integration, and impact on learning.Anat Sci Educ. 2014 Sep-Oct;7(5):350-60. doi: 10.1002/ase.1428. Epub 2013 Dec 20. Anat Sci Educ. 2014. PMID: 24376259
-
Integrating Radiology and Anatomy Teaching in Medical Education in the UK--The Evidence, Current Trends, and Future Scope.Acad Radiol. 2016 Apr;23(4):521-6. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2015.12.010. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Acad Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26970390 Review.
-
Enhancing learning approaches: practical tips for students and teachers.Med Teach. 2013 Jun;35(6):433-43. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2013.775413. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Med Teach. 2013. PMID: 23496121 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the integration of pre-mortem body donor imaging into a dissection-based medical anatomy course.BMC Med Educ. 2020 Oct 23;20(1):384. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02300-4. BMC Med Educ. 2020. PMID: 33097041 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of flipped classroom model in teaching histology for first-year MBBS students based on competency-based blended learning: An interventional study.J Educ Health Promot. 2021 May 20;10:152. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_467_20. eCollection 2021. J Educ Health Promot. 2021. PMID: 34222527 Free PMC article.
-
What works in radiology education for medical students: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Jan 10;24(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12909-023-04981-z. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 38200489 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of 3D-printed models prepared from radiological data for anatomy education: A meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis of 22 randomized, controlled, crossover trials.J Educ Health Promot. 2022 Oct 31;11:353. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_199_22. eCollection 2022. J Educ Health Promot. 2022. PMID: 36567994 Free PMC article.
-
Application of 3D-printed pulmonary segment specimens in experimental teaching of sectional anatomy.BMC Surg. 2023 May 4;23(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12893-023-02022-6. BMC Surg. 2023. PMID: 37142968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fink LD, Parmelee DX. Preface. In: Michaelsen LK, Parmenlee DX, Mcmahon KK, Levine RE, editors. Team-Based Learning for Health Professions Education. Virginia: Stylus; 2008.
-
- Regan de Bere S, Mattick K. From anatomical ‘competence’ to complex capability. The views and experiences of UK tutors on how we should teach anatomy to medical students. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2010;15:573–85. - PubMed
-
- Holt NF. Medical students need more radiology education. Acad Med. 2001;76:1. - PubMed
-
- Jeffrey DR, Goddard PR, Callaway MP, Greenwood R. Chest radiograph interpretation by medical students. Clin Radiol. 2003;58:478–81. - PubMed
-
- Pascual TN, Chhem R, Wang SC, Vujnovic S. Undergraduate radiology education in the era of dynamism in medical curriculum: An educational perspective. Eur J Radiol. 2011;78:319–25. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials