Principles of Aggregation-Induced Emission: Design of Deactivation Pathways for Advanced AIEgens and Applications
- PMID: 32154630
- PMCID: PMC7318703
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202000940
Principles of Aggregation-Induced Emission: Design of Deactivation Pathways for Advanced AIEgens and Applications
Abstract
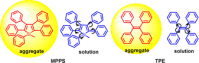
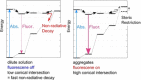
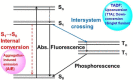
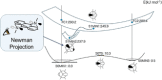
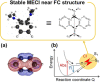
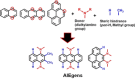
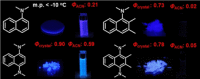
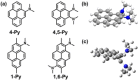
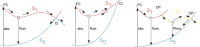
Twenty years ago, the concept of aggregation-induced emission (AIE) was proposed, and this unique luminescent property has attracted scientific interest ever since. However, AIE denominates only the phenomenon, while the details of its underlying guiding principles remain to be elucidated. This minireview discusses the basic principles of AIE based on our previous mechanistic study of the photophysical behavior of 9,10-bis(N,N-dialkylamino)anthracene (BDAA) and the corresponding mechanistic analysis by quantum chemical calculations. BDAA comprises an anthracene core and small electron donors, which allows the quantum chemical aspects of AIE to be discussed. The key factor for AIE is the control over the non-radiative decay (deactivation) pathway, which can be visualized by considering the conical intersection (CI) on a potential energy surface. Controlling the conical intersection (CI) on the potential energy surface enables the separate formation of fluorescent (CI:high) and non-fluorescent (CI:low) molecules [control of conical intersection accessibility (CCIA)]. The novelty and originality of AIE in the field of photochemistry lies in the creation of functionality by design and in the active control over deactivation pathways. Moreover, we provide a new design strategy for AIE luminogens (AIEgens) and discuss selected examples.
Keywords: aggregation-induced emission; bis(dialkylamino)anthracene; control of conical intersection accessibility.
© 2020 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- None
-
- Mei J., Leung N. L. C., Kwok R. T. K., Lam J. W. Y., Tang B. Z., Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11718–11940; - PubMed
-
- Mei J., Hong Y., Lam J. W. Y., Qin A., Tang Y., Tang B. Z., Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5429–5479; - PubMed
-
- Ding D., Li K., Liu B., Tang B. Z., Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2441–2453; - PubMed
-
- Chen Y., Lam J. W. Y., Kwok R. T. K., Liu B., Tang B. Z., Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 428–433;
Publication types
Grants and funding
- Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas 17H05145/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) 18H02045/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- Grant-in-Aid for JSPS Fellows 16J10324/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- JSPS Overseas Research Fellowships/Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- PRESTO (New Materials Science and Element Strategy)/Japan Science and Technology Agency
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

