Trends in the incidence and survival of patients with esophageal cancer: A SEER database analysis
- PMID: 32154652
- PMCID: PMC7180574
- DOI: 10.1111/1759-7714.13311
Trends in the incidence and survival of patients with esophageal cancer: A SEER database analysis
Abstract
Background: Recent studies have indicated that the incidence of esophageal cancer has declined in the past decade in the U.S. However, trends in the incidence and survival have not been thoroughly examined.
Methods: Data from 46 063 patients with esophageal cancer between 1973 and 2015 were collected from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database. The trends in the age-adjusted incidence and survival were analyzed using joinpoint regression models.
Results: The age-adjusted incidence of esophageal cancer increased from 5.55 to 7.44 per 100 000 person-years between 1973 and 2004. Later, it decreased at an annual percentage change of 1.23%. In the last 40 years, the strong male predominance increased slightly. Importantly, the percentage of patients with localized stage of squamous cell cancer decreased. It was observed that the incidence of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma declined since 1986, while the incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma sharply increased since 1973 and surpassed the rate of squamous cell cancer, mainly due to the increase in the incidence among men. Consistently, the estimated 40-year limited-duration prevalence of esophageal adenocarcinoma was higher than that of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Additionally, we observed a modest but significant improvement in survival during the study period.
Conclusion: The incidence of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma has decreased significantly over the past four decades in the U.S., while the incidence of adenocarcinoma has increased, particularly among men. Overall, the long-term survival of patients with esophageal cancer is poor but it has improved over the past decades, especially for the localized disease.
Key points: Significant findings of the study The incidence of esophageal cancer has decreased at an annual percentage change of 1.23% since 2004. The incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma has sharply increased since 1973 and surpassed the rate of squamous cell cancer, mainly due to the increase in the incidence among men. What this study adds There has been a shift in the prevalence of esophageal cancer histological subtypes over the past decades in the U.S. We found that the incidence of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma has continued to decrease, while the esophageal adenocarcinoma rate has continued to increase.
Keywords: SEER; esophageal cancer; incidence; prevalence; survival.
© 2020 The Authors. Thoracic Cancer published by China Lung Oncology Group and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
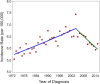
 observed,
observed,  1973–2004 APC = 0.56^,
1973–2004 APC = 0.56^,  2004–2015 APC = −1.23^.
2004–2015 APC = −1.23^.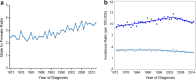
 Male – 1 Joinpoint,
Male – 1 Joinpoint,  1973–2004 APC = 0.77^,
1973–2004 APC = 0.77^,  2004–2015 APC = −1.24^.
2004–2015 APC = −1.24^.  Female –_Joinpoint,
Female –_Joinpoint,  1973–1996 APC = −0.04^,
1973–1996 APC = −0.04^,  1996–2015 APC = −1.24^. (^) Indicates the annual percent change (APC) that is significantly different from zero (P < 0.05).
1996–2015 APC = −1.24^. (^) Indicates the annual percent change (APC) that is significantly different from zero (P < 0.05).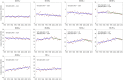

 Localized,
Localized,  regional,
regional,  distant,
distant,  unstaged. (b) esophageal squamous cell carcinoma,
unstaged. (b) esophageal squamous cell carcinoma,  Localized,
Localized,  regional,
regional,  distant,
distant,  unstaged. and (c) esophageal adenocarcinoma.
unstaged. and (c) esophageal adenocarcinoma.  Localized,
Localized,  regional,
regional,  distant,
distant,  unstaged.
unstaged.
 Squamous – 1 Joinpoint,
Squamous – 1 Joinpoint,  1973–1985 APC = 0.30,
1973–1985 APC = 0.30,  1985–2015 APC = −3.08^;
1985–2015 APC = −3.08^;  Adenocarcinoma – 1 Joinpoint,
Adenocarcinoma – 1 Joinpoint,  1973–1999 APC = 7.82^,
1973–1999 APC = 7.82^,  1999–2015 APC = 0.58^;
1999–2015 APC = 0.58^;  other – 2 joinpoints,
other – 2 joinpoints,  1973–1983 APC = −4.80^,
1973–1983 APC = −4.80^,  1983–2009 APC = −0.19,
1983–2009 APC = −0.19,  2009–2015 APC = −6.30^.
2009–2015 APC = −6.30^.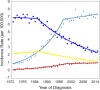
 Male/Squamous – 1 Joinpoint,
Male/Squamous – 1 Joinpoint,  1973–1985 APC = −0.15,
1973–1985 APC = −0.15,  1985–2015 APC = −3.49^;
1985–2015 APC = −3.49^;  Male/Adenocarcinoma – 1 Joinpoint,
Male/Adenocarcinoma – 1 Joinpoint,  1973–1998 APC = 8.25^,
1973–1998 APC = 8.25^,  1998–2015 APC = 0.59^,
1998–2015 APC = 0.59^,  Female/Squamous – 1 Joinpoint,
Female/Squamous – 1 Joinpoint,  1973–1986 APC = −0.96,
1973–1986 APC = −0.96,  1986–2015 APC = −2.52^,
1986–2015 APC = −2.52^,  Female/Adenocarcinoma – 1 Joinpoint,
Female/Adenocarcinoma – 1 Joinpoint,  1973–1999 APC = 7.27^,
1973–1999 APC = 7.27^,  1999–2015 APC = 0.84.
1999–2015 APC = 0.84.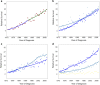
 observed,
observed,  1973–1992 APC = 6.28^,
1973–1992 APC = 6.28^,  1992–2010 APC = 3.31^, and stratified by (b) sex,
1992–2010 APC = 3.31^, and stratified by (b) sex,  Male – 1 Joinpoint,
Male – 1 Joinpoint,  1973–1992 APC = 7.19^;
1973–1992 APC = 7.19^;  1992–2010 APC = 3.42^,
1992–2010 APC = 3.42^,  Female – 0 Joinpoints,
Female – 0 Joinpoints,  1973–2010 APC = 3.52^, (c) histology,
1973–2010 APC = 3.52^, (c) histology,  Squamous – 1 joinpoint,
Squamous – 1 joinpoint,  1973–1985 APC = 8.02^,
1973–1985 APC = 8.02^,  1985–2010 APC = 2.92^,
1985–2010 APC = 2.92^,  Adenocarcinoma – 1 Joinpoint,
Adenocarcinoma – 1 Joinpoint,  1975–2002 APC = 5.44^,
1975–2002 APC = 5.44^,  2002–2010 APC = 1.50, or (d) stage,
2002–2010 APC = 1.50, or (d) stage,  Localised – 1 Joinpoint,
Localised – 1 Joinpoint,  1973–1983 APC = 11.06^,
1973–1983 APC = 11.06^,  1983–2010 APC = 4.45^,
1983–2010 APC = 4.45^,  Regional – 0 Joinpoints,
Regional – 0 Joinpoints,  1973–2010 APC = 5.48^,
1973–2010 APC = 5.48^,  Distant – invalid data. (^) Indicates the annual percent change (APC) that is significantly different from zero (P < 0.05).
Distant – invalid data. (^) Indicates the annual percent change (APC) that is significantly different from zero (P < 0.05).References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet‐Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 2015; 65 (2): 87–108. - PubMed
-
- Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA, Luketich JD. Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet 2013; 381 (9864): 400–12. - PubMed
-
- Thrift AP, Whiteman DC. The incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma continues to rise: analysis of period and birth cohort effects on recent trends. Ann Oncol 2012; 23 (12): 3155–62. - PubMed
-
- Dubecz A, Solymosi N, Stadlhuber RJ, Schweigert M, Stein HJ, Peters JH. Does the incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and gastric cardia continue to rise in the twenty‐first century?‐a SEER database analysis. J Gastrointest Surg 2013; 18(1): 124–129. - PubMed
-
- Castro C, Bosetti C, Malvezzi M et al Patterns and trends in esophageal cancer mortality and incidence in Europe (1980‐2011) and predictions to 2015. Ann Oncol 2014; 25 (1): 283–90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

