Participation and Performance Trends in the Oldest 100-km Ultramarathon in the World
- PMID: 32155703
- PMCID: PMC7084458
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17051719
Participation and Performance Trends in the Oldest 100-km Ultramarathon in the World
Abstract
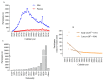
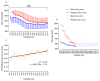
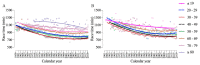
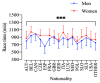
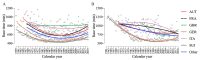
Participation and performance trends in ultramarathon running have been investigated for large datasets and long period of times with an increase in participants and an improvement in performance. However, the analysis of ultramarathons across many decades is missing. We analyzed these trends for 96,036 athletes (88,286 men and 7750 women) from 67 countries competing between 1956 and 2019 in '100 km Lauf Biel' in Switzerland, the oldest 100-km ultramarathon in the world. More men than women participated in all years. The number of male participants reached a peak at around 1985 and a decline in participation occurred thereafter. Women started competing in 1962. Men were always faster than women and both women and men reduced their race times over years. After about 1985, both overall women and men and both female and male winners were not able to improve race times. For men, athletes from all age groups below the age of 49 years old reached a peak of participation in the 1980s, and showed a decrease since then. Regarding age groups, the decrease first started in age group 20-29 years, followed by 30-39, 40-49, 50-59, and 60-69 years. For athletes in age groups 70-79 and 80-89 years, no decrease occurred. For women, age group athletes in age groups 40-49, 50-59, and 60-69 years increased their participation, whereas age groups 20-29 and 30-39 peaked in the late 1980s and started to decrease or stabilize, respectively. Switzerland, Germany, and France were the countries with the highest numbers of participants throughout the history of the race. In men, race times increased after about 1990 for most nationalities; only runners from Germany seemed to stabilize their performance. In women, runners from Italy, France, and Austria improved their performance over the years. In summary, the analysis of the oldest 100-km ultramarathon in the world showed a decrease in participation and an impairment in performance in the last 60 years. These changes were due to a decrease in the number of male ultramarathoners in around the 1980s, where mainly the number of age group runners younger than 70 years decreased.
Keywords: age group; motivation; nationality; running; sex; ultra-endurance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

