Combined wIRA-Hyperthermia and Hypofractionated Re-Irradiation in the Treatment of Locally Recurrent Breast Cancer: Evaluation of Therapeutic Outcome Based on a Novel Size Classification
- PMID: 32155740
- PMCID: PMC7139693
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12030606
Combined wIRA-Hyperthermia and Hypofractionated Re-Irradiation in the Treatment of Locally Recurrent Breast Cancer: Evaluation of Therapeutic Outcome Based on a Novel Size Classification
Abstract
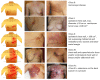
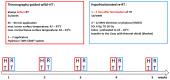
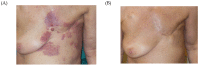
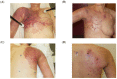
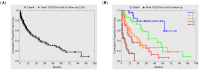
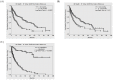
Effective tumor control in patients suffering from unresectable locally recurrent breast cancer (LRBC) in pre-irradiated areas can be achieved by re-irradiation combined with superficial hyperthermia. Using this combined modality, total re-irradiation dose and toxicity can be significantly reduced compared to conventionally fractionated treatment schedules with total doses of 60-66 Gy. Applying contact-free, thermography-controlled water-filtered infrared-A superficial hyperthermia, immediately followed by hypofractionated re-irradiation, consisting of 4 Gy once per week up to a total dose of 20 Gy, resulted in high overall response rates even in large-sized tumors. Comparability of clinical data between different combined Hyperthermia (HT)/Radiotherapy (RT) treatment schedules is impeded by the highly individual characteristics of this disease. Tumor size, ranging from microscopic disease and small lesions to large-sized cancer en cuirasse, is described as one of the most important prognostic factors. However, in clinical studies and analyses of LRBC, tumor size has so far been reported in a very heterogeneous way. Therefore, we suggest a novel, simple and feasible size classification (rClasses 0-IV). Applying this classification for the evaluation of 201 patients with pre-irradiated LRBC allowed for a stratification into distinct prognostic groups.
Keywords: LRBC; clinical outcome; locally recurrent breast cancer; novel size classification; re-irradiation; superficial hyperthermia; toxicity; wIRA hyperthermia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest and no competing financial interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Notter M., Piazena H., Vaupel P. Hypofractionated re-irradiation of large-sized recurrent breast cancer with thermography-controlled, contact-free water-filtered infra-red-A hyperthermia: A retrospective study of 73 patients. Int. J. Hyperth. 2017;33:227–236. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2016.1235731. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Oldenborg S., Rasch C.R.N., Os R.V., Kusumanto Y.H., Oei B.S., Venselaar J.L., Heymans M.W., Zum Vörde Sive Vörding P.J., Crezee H., Tienhoven G.V. Reirradiation + hyperthermia for recurrent breast cancer en cuirasse. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2017;194:206–214. doi: 10.1007/s00066-017-1241-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

