Fosfomycin Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolates from South Korea and in vitro Activity of Fosfomycin Alone and in Combination with Other Antibiotics
- PMID: 32155809
- PMCID: PMC7148487
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics9030112
Fosfomycin Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolates from South Korea and in vitro Activity of Fosfomycin Alone and in Combination with Other Antibiotics
Abstract
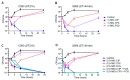
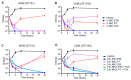
We investigated fosfomycin susceptibility in Escherichia coli clinical isolates from South Korea, including community-onset, hospital-onset, and long-term care facility (LTCF)-onset isolates. The resistance mechanisms and genotypes of fosfomycin-resistant isolates were also identified. Finally, the in vitro efficacy of combinations of fosfomycin with other antibiotics were examined in susceptible or extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing E. coli isolates. The fosfomycin resistance rate was 6.7% and was significantly higher in LTCF-onset isolates than community-onset and hospital-onset isolates. Twenty-one sequence types (STs) were identified among 19 fosfomycin-resistant E. coli isolates, showing diverse genotypes. fosA3 was found in only two isolates, and diverse genetic variations were identified in three genes associated with fosfomycin resistance, namely, GlpT, UhpT, and MurA. Some fosfomycin-resistant E. coli isolates carried no mutations. In vitro time-kill assays showed that fosfomycin alone did not exhibit an excellent killing activity, compared with ciprofloxacin in susceptible isolates and with ertapenem in ESBL producers. However, combining fosfomycin with cefixime or piperacillin-tazobactam eradicated susceptible or ESBL-producing isolates, respectively, even with 0.5× minimum inhibitory concentrations. Overall, we found a relatively high fosfomycin resistance rate in E. coli isolates from South Korea. Based on their genotypes and resistance mechanisms, most of the fosfomycin-resistant E. coli isolates might occur independently. Antibiotic combinations with fosfomycin could be a suitable therapeutic option for infections caused by E. coli isolates.
Keywords: cefixime; fosfomycin; in vitro time-kill; piperacillin-tazobactam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial susceptibility and mechanisms of fosfomycin resistance in extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli strains from urinary tract infections in Wenzhou, China.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2017 Jul;50(1):29-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2017.02.010. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2017. PMID: 28456703
-
Characterization of Fosfomycin Resistant Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Isolates from Human and Pig in Taiwan.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 17;10(8):e0135864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135864. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26280832 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro susceptibility pattern of cephalosporin-resistant Gram-negative bacteria.J Med Assoc Thai. 2008 Oct;91 Suppl 3:S21-7. J Med Assoc Thai. 2008. PMID: 19255989
-
Other antimicrobials of interest in the era of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: fosfomycin, nitrofurantoin and tigecycline.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008 Jan;14 Suppl 1:198-202. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01852.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008. PMID: 18154548 Review.
-
Treatment of urinary tract infections in the era of antimicrobial resistance and new antimicrobial agents.Postgrad Med. 2020 Apr;132(3):234-250. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2019.1680052. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Postgrad Med. 2020. PMID: 31608743 Review.
Cited by
-
High-Frequency Detection of fosA3 and bla CTX-M-55 Genes in Escherichia coli From Longitudinal Monitoring in Broiler Chicken Farms.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 18;13:846116. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.846116. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35663865 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of Urinary Extended-spectrum β-lactamase Escherichia coli to Fosfomycin.Oman Med J. 2021 Nov 10;36(6):e314. doi: 10.5001/omj.2021.95. eCollection 2021 Nov. Oman Med J. 2021. PMID: 34804597 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Chromosomal Mutations Responsible for Fosfomycin Resistance in Escherichia coli.Front Microbiol. 2020 Oct 20;11:575031. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.575031. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33193186 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Antibiotics for Bacteremia and Infective Endocarditis: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives.Microorganisms. 2023 Dec 18;11(12):3004. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11123004. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38138148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fosfomycin as Partner Drug for Systemic Infection Management. A Systematic Review of Its Synergistic Properties from In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Aug 10;9(8):500. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9080500. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32785114 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bouchillon S.K., Badal R.E., Hoban D.J., Hawser S.P. Antimicrobial susceptibility of inpatient urinary tract isolates of gram-negative bacilli in the United States: Results from the study for monitoring antimicrobial resistance trends (SMART) program: 2009–2011. Clin. Ther. 2013;35:872–877. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2013.03.022. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

