Expression and Significance of MicroRNA155 in Serum of Patients with Cerebral Small Vessel Disease
- PMID: 32156102
- PMCID: PMC7365280
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2019.0179
Expression and Significance of MicroRNA155 in Serum of Patients with Cerebral Small Vessel Disease
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the changes and significance of microRNA155 levels in serum of patients with cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD).
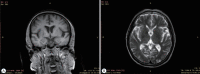
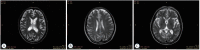
Methods: Thirty patients with CSVD who met the inclusion criteria were selected and divided into eight patients with lacunar infarction (LI) group and 22 patients with multiple lacunar infarction (MLI) combined with white matter lesions (WML) group according to the results of head magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Thirty samples from healthy volunteers without abnormalities after head MRI examination were selected as the control group. The levels of serum microRNA155 in each group were determined by real-time polymerase chain reaction, and the correlation between microRNA155 in the serum of patients with CSVD and the increase of imaging lesions was analyzed by Spearman correlation analysis.
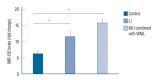
Results: Compared with the control group, the serum microRNA155 level in the LI group, MLI combined with WML group increased, the difference was statistically significant (p<0.05); serum microRNA155 level was positively correlated with the increase of imaging lesions (p<0.05).
Conclusion: The change of serum microRNA155 level in patients with CSVD may be one of its self-protection mechanisms, and the intensity of this self-protection mechanism is positively correlated with the number of CSVD lesions.
Keywords: Cerebral small vessel disease; Real-time polymerase chain reaction; Self protection mechanism.; Serum; microRNA155 level.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Ago T. The neurovascular unit in health and ischemic stroke. Nihon Rinsho. 2016;74:583–588. - PubMed
-
- Cerebrovascular disease group of Neurology branch of Chinese Medical Association. Neurology Branch of Chinese Medical Association Consensus on diagnosis and treatment of cerebrovascular disease in China. Chin J Neurol. 2015;48:838–844.
-
- Chiu AP, Wan A, Lal N, Zhang D, Wang F, Vlodavsky I, et al. Cardiomyocyte VEGF regulates endothelial cell GPIHBP1 to relocate lipoprotein lipase to the coronary lumen during diabetes mellitus. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016;36:145–155. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

