Motor neuron preservation and decrease of in vivo TDP-43 phosphorylation by protein CK-1δ kinase inhibitor treatment
- PMID: 32157143
- PMCID: PMC7064575
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-61265-y
Motor neuron preservation and decrease of in vivo TDP-43 phosphorylation by protein CK-1δ kinase inhibitor treatment
Abstract
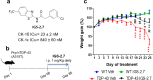
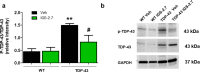
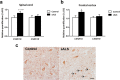
Pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), a devastating disease where no treatment exists, involves the compartmentalization of the nuclear protein TDP-43 (TAR DNA-binding protein 43) in the cytoplasm which is promoted by its aberrant phosphorylation and others posttranslational modifications. Recently, it was reported that CK-1δ (protein casein kinase-1δ) is able to phosphorylate TDP-43. Here, the preclinical efficacy of a benzothiazole-based CK-1δ inhibitor IGS-2.7, both in a TDP-43 (A315T) transgenic mouse and in a human cell-based model of ALS, is shown. Treatment with IGS-2.7 produces a significant preservation of motor neurons in the anterior horn at lumbar level, a decrease in both astroglial and microglial reactivity in this area, and in TDP-43 phosphorylation in spinal cord samples. Furthermore, the recovery of TDP-43 homeostasis (phosphorylation and localization) in a human-based cell model from ALS patients after treatment with IGS-2.7 is also reported. Moreover, we have shown a trend to increase in CK-1δ mRNA in spinal cord and significantly in frontal cortex of sALS cases. All these data show for the first time the in vivo modulation of TDP-43 toxicity by CK-1δ inhibition with IGS-2.7, which may explain the benefits in the preservation of spinal motor neurons and point to the relevance of CK-1δ inhibitors in a future disease-modifying treatment for ALS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Targeting TDP-43 phosphorylation by Casein Kinase-1δ inhibitors: a novel strategy for the treatment of frontotemporal dementia.Mol Neurodegener. 2016 Apr 30;11(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s13024-016-0102-7. Mol Neurodegener. 2016. PMID: 27138926 Free PMC article.
-
CK1δ/ε-mediated TDP-43 phosphorylation contributes to early motor neuron disease toxicity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024 Dec 4;12(1):187. doi: 10.1186/s40478-024-01902-z. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024. PMID: 39633494 Free PMC article.
-
Novel group-based QSAR and combinatorial design of CK-1δ inhibitors as neuroprotective agents.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Dec 22;17(Suppl 19):515. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1379-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 28155653 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular link between inefficient GluA2 Q/R site-RNA editing and TDP-43 pathology in motor neurons of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients.Brain Res. 2014 Oct 10;1584:28-38. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2013.12.011. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24355598 Review.
-
Review: Prion-like mechanisms of transactive response DNA binding protein of 43 kDa (TDP-43) in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2015 Aug;41(5):578-97. doi: 10.1111/nan.12206. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25487060 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of Mitophagy Inhibitors with Therapeutic Potential in Different Familial Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Mutations.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 21;23(20):12676. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012676. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293534 Free PMC article.
-
Critical impact of lysine 136 in TDP-43 phase separation, compartmentalization, and aggregation in living vertebrates.iScience. 2025 May 27;28(7):112761. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112761. eCollection 2025 Jul 18. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40585370 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the TDP-43 Proteinopathy Pathway From Neurons to Muscle: Physiological and Pathophysiological Functions.Front Neurosci. 2022 Feb 3;16:815765. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.815765. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35185458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Alterations in Sporadic and SOD1-ALS Immortalized Lymphocytes: Towards a Personalized Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 16;22(6):3007. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063007. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33809456 Free PMC article.
-
TTBK1 and CK1 inhibitors restore TDP-43 pathology and avoid disease propagation in lymphoblast from Alzheimer's disease patients.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Aug 9;16:1243277. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1243277. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37621404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Palomo, V. et al. TDP-43: A Key Therapeutic Target beyond Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. ACS Chem Neurosci.10(3), 1183–1196 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

