An integrative analysis of 5HTT-mediated mechanism of hyperactivity to non-threatening voices
- PMID: 32157156
- PMCID: PMC7064530
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-020-0850-3
An integrative analysis of 5HTT-mediated mechanism of hyperactivity to non-threatening voices
Abstract
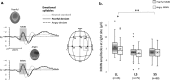
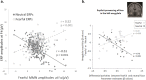
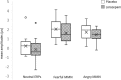
The tonic model delineating the serotonin transporter polymorphism's (5-HTTLPR) modulatory effect on anxiety points towards a universal underlying mechanism involving a hyper-or-elevated baseline level of arousal even to non-threatening stimuli. However, to our knowledge, this mechanism has never been observed in non-clinical cohorts exhibiting high anxiety. Moreover, empirical support regarding said association is mixed, potentially because of publication bias with a relatively small sample size. Hence, how the 5-HTTLPR modulates neural correlates remains controversial. Here we show that 5-HTTLPR short-allele carriers had significantly increased baseline ERPs and reduced fearful MMN, phenomena which can nevertheless be reversed by acute anxiolytic treatment. This provides evidence that the 5-HTT affects the automatic processing of threatening and non-threatening voices, impacts broadly on social cognition, and conclusively asserts the heightened baseline arousal level as the universal underlying neural mechanism for anxiety-related susceptibilities, functioning as a spectrum-like distribution from high trait anxiety non-patients to anxiety patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interaction effects of the 5-HTT and MAOA-uVNTR gene variants on pre-attentive EEG activity in response to threatening voices.Commun Biol. 2022 Apr 8;5(1):340. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03297-w. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35396540 Free PMC article.
-
'Negativity bias' in risk for depression and anxiety: brain-body fear circuitry correlates, 5-HTT-LPR and early life stress.Neuroimage. 2009 Sep;47(3):804-14. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.05.009. Epub 2009 May 14. Neuroimage. 2009. PMID: 19446647
-
Relationship of the serotonin transporter gene promoter polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) genotype and serotonin transporter binding to neural processing of negative emotional stimuli.J Affect Disord. 2016 Jan 15;190:494-498. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2015.10.047. Epub 2015 Nov 4. J Affect Disord. 2016. PMID: 26561939 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin transporter polymorphisms (5-HTTLPR) in emotion processing: implications from current neurobiology.Prog Neurobiol. 2014 Jun;117:41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2014.02.003. Epub 2014 Feb 16. Prog Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24548605 Review.
-
Looking on the bright side of serotonin transporter gene variation.Biol Psychiatry. 2011 Mar 15;69(6):513-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.09.024. Epub 2010 Nov 2. Biol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21047622 Review.
Cited by
-
Application and Mechanisms of Internet-Based Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (iCBT) in Improving Psychological State in Cancer Patients.J Cancer. 2023 Jul 3;14(11):1981-2000. doi: 10.7150/jca.82632. eCollection 2023. J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37497400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Negative emotionality downregulation affects moral choice but not moral judgement of harm: a pharmacological study.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 12;14(1):1200. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51345-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38216629 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction effects of the 5-HTT and MAOA-uVNTR gene variants on pre-attentive EEG activity in response to threatening voices.Commun Biol. 2022 Apr 8;5(1):340. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03297-w. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35396540 Free PMC article.
-
The Multifaceted Effects of Serotonin Transporter Polymorphism (5-HTTLPR) on Anxiety, Implicit Moral Attitudes, and Harmful Behaviors.Front Psychol. 2020 Jul 10;11:1521. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01521. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32754089 Free PMC article.

