ADAR1-mediated RNA editing is a novel oncogenic process in thyroid cancer and regulates miR-200 activity
- PMID: 32157211
- PMCID: PMC7190574
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-020-1248-x
ADAR1-mediated RNA editing is a novel oncogenic process in thyroid cancer and regulates miR-200 activity
Abstract
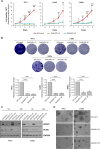
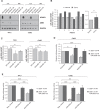
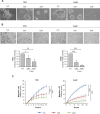
Adenosine deaminases acting on RNA (ADARs) convert adenosine to inosine in double-stranded RNA. A-to-I editing of RNA is a widespread posttranscriptional process that has recently emerged as an important mechanism in cancer biology. A-to-I editing levels are high in several human cancers, including thyroid cancer, but ADAR1 editase-dependent mechanisms governing thyroid cancer progression are unexplored. To address the importance of RNA A-to-I editing in thyroid cancer, we examined the role of ADAR1. Loss-of-function analysis showed that ADAR1 suppression profoundly repressed proliferation, invasion, and migration in thyroid tumor cell models. These observations were validated in an in vivo xenograft model, which showed that ADAR1-silenced cells had a diminished ability to form tumors. RNA editing of miRNAs has the potential to markedly alter target recognition. According to TCGA data, the tumor suppressor miR-200b is overedited in thyroid tumors, and its levels of editing correlate with a worse progression-free survival and disease stage. We confirmed miR-200b overediting in thyroid tumors and we showed that edited miR-200b has weakened activity against its target gene ZEB1 in thyroid cancer cells, likely explaining the reduced aggressiveness of ADAR1-silenced cells. We also found that RAS, but not BRAF, modulates ADAR1 levels, an effect mediated predominantly by PI3K and in part by MAPK. Lastly, pharmacological inhibition of ADAR1 activity with the editing inhibitor 8-azaadenosine reduced cancer cell aggressiveness. Overall, our data implicate ADAR1-mediated A-to-I editing as an important pathway in thyroid cancer progression, and highlight RNA editing as a potential therapeutic target in thyroid cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

