Integrating Individual and Contextual Factors to Explain Disparities in HIV/STI Among Heterosexual African American Youth: A Contemporary Literature Review and Social Ecological Model
- PMID: 32157486
- PMCID: PMC7321914
- DOI: 10.1007/s10508-019-01609-6
Integrating Individual and Contextual Factors to Explain Disparities in HIV/STI Among Heterosexual African American Youth: A Contemporary Literature Review and Social Ecological Model
Abstract
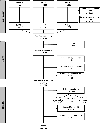
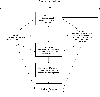
Heterosexual African American youth face substantial disparities in sexual health consequences such as HIV and STI. Based on the social ecological framework, the current paper provides a comprehensive, narrative review of the past 14 years of literature examining HIV/STI risk, including risky sexual behavior, among heterosexual African American youth and a conceptual model of risk among this population. The review found that individual psychological and biological factors are insufficient to explain the sexual health disparities faced by this group; instead, structural disadvantage, interpersonal risk, and community dysfunction contribute to the disparity in HIV/STI outcomes directly and indirectly through individual psychological factors. The conceptual model presented suggests that for African American youth, (1) HIV/STI risk commonly begins at the structural level and trickles down to the community, social, and individual levels, (2) risk works in a positive feedback system such that downstream effects compound the influence of structural risks, and (3) contextual and individual risk factors must be considered within the advanced stage of the epidemic facing this population. Despite advanced HIV and STI epidemics among heterosexual African American youth, multisystemic interventions that target structural risk factors and their downstream effects are posited to reduce the disparity among this high-risk population.
Keywords: African American; HIV risk; Risky sexual behavior; STI; Youth.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Adimora AA, & Schoenbach VJ (2002). Contextual factors and the black-white disparity in heterosexual HIV transmission. Epidemiology, 13(6), 707–712. - PubMed
-
- Adimora AA, & Schoenbach VJ (2005). Social context, sexual networks, and racial disparities in rates of sexually transmitted infections. The Journal of infectious diseases, 191(Supplement_1), S115–S122. - PubMed
-
- Alleyne B, & Gaston G (2010). Gender disparity and HIV risk among young Black women in college: A literature review. Affilia: Journal of Women & Social Work, 25(2), 135–145. doi:10.1177/0886109910364348 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

