pH-dependent secondary structure propensity of the influenza A virus M2 cytoplasmic tail
- PMID: 32157574
- PMCID: PMC7069904
- DOI: 10.1007/s12104-020-09937-8
pH-dependent secondary structure propensity of the influenza A virus M2 cytoplasmic tail
Abstract
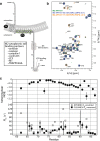
The cytoplasmic C-terminal tail of the matrix protein 2 (M2) from influenza A virus has a well conserved sequence and is involved in interactions with several host proteins as well as the influenza matrix protein 1 (M1). Whereas the transmembrane domain of M2 has been well characterised structurally and functionally, high resolution information about the distal cytoplasmic tail is lacking. Here we report the chemical shifts of the cytoplasmic tail of M2 and the chemical shift perturbations at low pH and in the presence of membrane mimetics. The cytoplasmic tail residues are mostly disordered but an extended backbone conformation is adopted by the LC3 binding motif and the putative M1 interaction site has partial helical content with a small pH-dependence. The chemical shift assignments provide a basis for further investigations into interactions of the M2 cytoplasmic tail with viral and host cell factors.
Keywords: Influenza; M2; Matrix protein 2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cho KJ, Schepens B, Seok JH, Kim S, Roose K, Lee JH, Gallardo R, Van Hamme E, Schymkowitz J, Rousseau F, Fiers W, Saelens X, Kim KH. Structure of the extracellular domain of matrix protein 2 of influenza A virus in complex with a protective monoclonal antibody. J Virol. 2015;89(7):3700–3711. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02576-14. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

